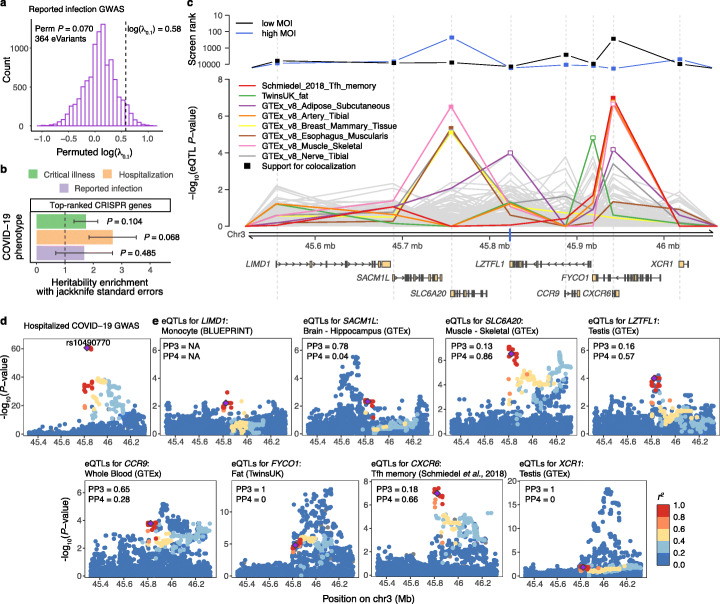
Fig. 1.
Genetic regulatory effects of top-ranked CRISPR genes and prioritization of genes in the 3p21.31 locus associated with COVID-19 GWAS. a Histogram of the permuted log(λ0.1) to test the significance of the inflation in reported SARS-CoV-2 infection GWAS for variants that are cis-eQTLs for top-ranked CRISPR genes in Lung (n = 364). Vertical dashed line denotes the observed log(λ0.1) value. b Heritability enrichment in top-ranked genes from the CRISPR screen for the three main COVID-19 phenotypes. Vertical dashed line denotes no enrichment. c Prioritization of genes in the 3p21.31 locus by integrating CRISPR screens and cis-eQTLs. The top panel shows the ranking of the genes in the locus according to the second-best guide RNA score in the low MOI (black) and high MOI (blue) pooled CRISPR screens. The middle panel shows the cis-eQTL P values for the lead GWAS variant in the 3p21.31 locus (rs10490770, denoted as a blue tick on the x-axis) in different cell types and tissues from the eQTL Catalogue and GTEx, 112 eQTL data sets in total. Highlighted are eight cell types/tissues, where the cis-eQTL P value for the lead GWAS variant is < 10−4 for at least one gene in the region. Filled square denotes support for colocalization between the GWAS and cis-eQTL signal (posterior probability for one shared causal variant (PP4) > 0.5). The bottom panel depicts the transcripts of the eight protein-coding genes in the locus. Ranks and cis-eQTL P values are aligned to match the start of the gene which is shown as a gray dashed line across the panels. d, e Regional association plots of the hospitalized COVID-19 GWAS (d) and cis-eQTLs for the eight genes (e) from the associated locus in the cell type/tissue where the lead GWAS variant has the lowest cis-eQTL P value. Purple diamond denotes the lead GWAS variant, and the data points are colored based on the (weighted average) LD between the lead GWAS variant and other variants in the region in the respective study population. PP3 and PP4—posterior probability for two different variants or one shared causal variant in coloc, respectively