Figure 4.
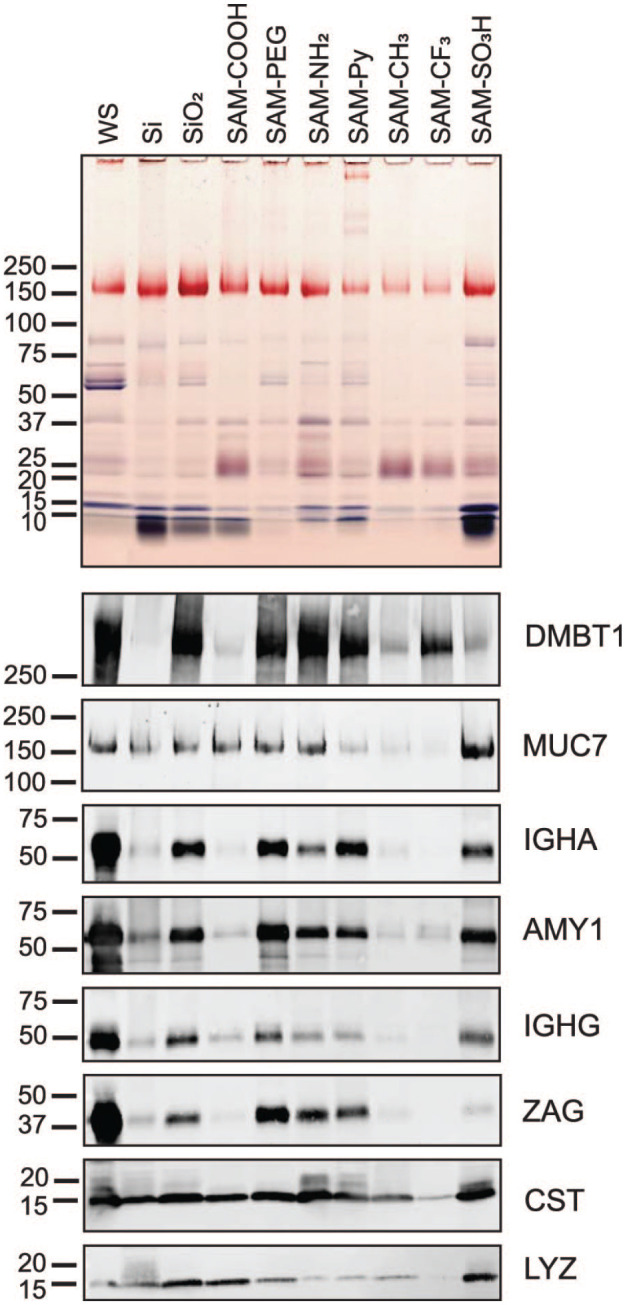
SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis of proteins from saliva adsorbed to chemically modified Si beads. Salivary proteins adsorbed to untreated (Si) and oxidized silica beads (SiO2) as well as to beads modified with 7 chemical functionalities were eluted from the silica bead surface by heating in SDS. Optimal time points for complete protein adsorption were obtained in kinetic studies (Appendix Fig. 6). Equal volumes of eluates were separated by SDS-PAGE. The original whole saliva (WS) that was used for adsorption was run for comparison (first lane). Proteins in the gel were stained with Coomassie blue, and glycans on glycoproteins were revealed by periodic acid–Schiff stain (pink bands). Nitrocellulose transfers from gel replicates were probed with antibodies against salivary agglutinin (DMBT1), mucin 7 (MUC7), immunoglobulin A heavy chain (IGHA), salivary α-amylase (AMY1), immunoglobulin G heavy chain Fc portion (IGHG), zinc-α2-glycoprotein (ZAG), cystatins (CST), and lysozyme (LYZ). Bound primary antibodies were detected with Alexa Fluor 488–tagged IgG secondary antisera.
