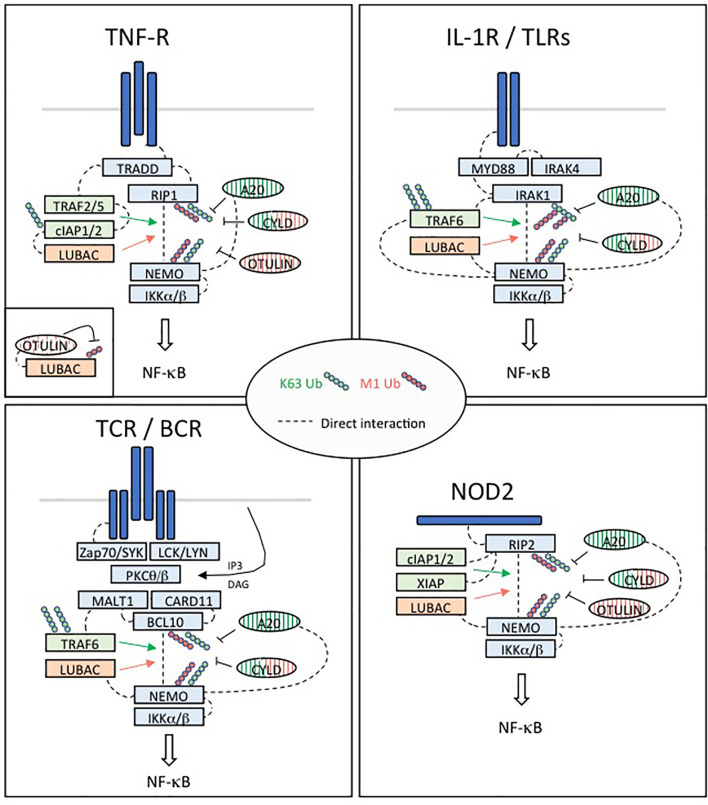
Figure 4.
Regulation of NF-κB activation in four different pathways implicated in immune tolerance. TNFR: Upon binding of TNFα, the TNFR1 receptor trimerizes resulting in the recruitment of TRADD to the death domain (DD) of the receptors cytoplasmic tail. RIP1 is recruited through TRADD and TNFR1 through homotypic DD interactions. High affinity binding of TRAF2 trimers to TRADD is augmented by TRAF2/RIP1 interactions. TRAF2 trimers recruit cIAP1/2, which in turn recruit the LUBAC complex (HOIP, HOIL-1 and SHARPIN), while RIP1 mediates recruitment of TAK1 and the IKK complex through NEMO. This signaling complex (complex I) signals to NF-κB by recruiting in proximity TAK1 and the IKK complex supporting phosphorylation and activation of IKK. The ubiquitin ligase cIAP1/2 and LUBAC may facilitate TAK1 and IKK activation through production of linear and/or K63 linked ubiquitination. Then, activated IKK phosphorylates IκBα leading its ubiquitination and degradation and nuclear translocation of p65:p50 NF-κB complexes. DNA bound canonical NF-κB induces transcription of immune response genes as well as genes that protect the cell from TNF induced cell death. IL1R/TLRs: Despite differences in their extracellular domains, the IL-1 receptor (IL-1R) and TLRs contain a common cytoplasmic motif termed the Toll/IL-1R (TIR) homology domain, which is required for activation of NF-κB signaling pathways. IL-1R- and TLR-mediated NF-κB activation is initiated by the recruitment of MyD88 to the TIR. MyD88 is a scaffold protein that recruits the death domain-containing protein IRAK-1, IRAK-2, IRAK-4, and the ubiquitin protein ligase (E3) TRAF6. IRAK-4 and TRAF6 are essential signaling components of IL-1R- and TLR-mediated MAPK and NF-κB activation. IRAK-1 also plays an important role in IL-1R/TLR signaling in order to induce IKK activation and subsequently IκB activation and NF-κB nuclear translocation. TCR/BCR: In response to TCR or BCR triggering, phosphorylation of CARD11 (CARMA1) by PKC-θ or PKC-β on different Serine residues of its linker domain modifies its conformation allowing its association with a constitutively associated dimer formed by BCL10 and MALT1, leading to the assembly of the CBM complex. The formation of this complex constitutes one of the important steps towards NF-κB stimulation following TCR/BCR engagement. In turn, this complex activates the IκB kinase (IKK) responsible for the phosphorylation of the inhibitory factors IκBα and their subsequent degradation, allowing activation and nuclear translocation of NF-κB followed by transcription of its target genes. In addition to its scaffold function during NF-κB signaling, the paracaspase MALT1 exerts a proteolytic activity to ensure the regulation of NF-κB activation. NOD2: NOD2 immune function drive a higher incidence of autoimmune diseases such as Crohn’s disease. NOD2-mediated signaling relies on RIP2. RIP2 recruits a number of signaling regulators to the NOD2-associated protein complex, including several ubiquitin E3 ligases such as XIAP, c-IAP1/2, Pellino3, and LUBAC, which promote diverse ubiquitination of RIP2. XIAP is a critical ubiquitin ligase in the NOD2-RIP2 inflammatory pathway and promotes NEMO/IKK- mediated NF-κB activation.