Figure 4.
Vulnerability predictions correlate with the magnitude of target knockdown needed to reduce bacterial fitness
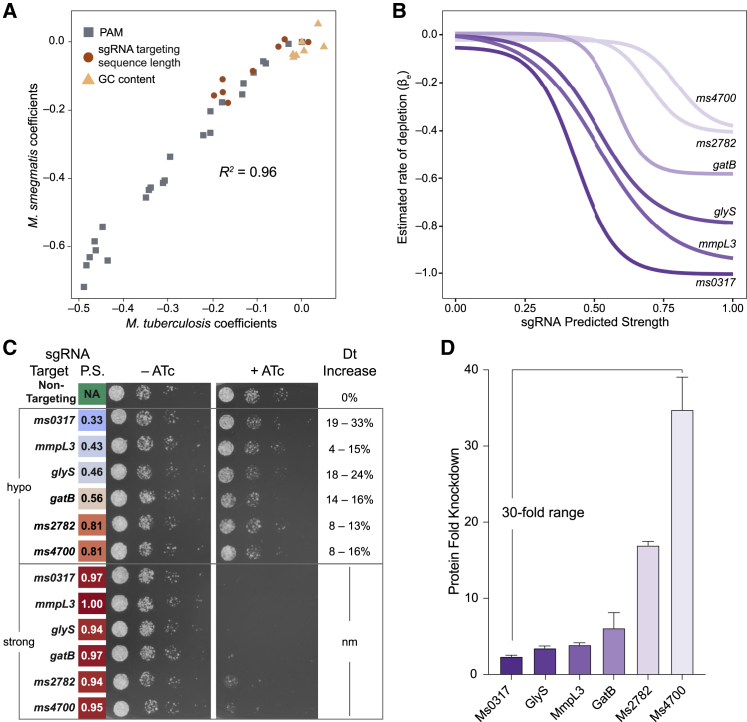
(A) Scatterplot of the linear model coefficients (as in Figure 2B) for Mtb H37Rv (x axis) and Msmeg (y axis).
(B) Mean logistic regression fits for the indicated Msmeg genes of varying vulnerability.
(C) Phenotypic consequences of hypomorphic (hypo) and strong knockdown of the genes depicted in (B). Predicted sgRNA strengths (P.S.) are listed next to each sgRNA and are color coded according to the scale in Figure 2D. The percent increase in strain doubling time (Dt) of each hypo sgRNA compared with a non-targeting control (95% confidence interval [CI]) was quantified at steady-state growth (Figure S3I). nm, not measured.
(D) Quantification of target gene protein levels (mean ± SD) by label-free mass spectrometry (+ATc) of the 6 hypo strains depicted in (C). qRT-PCR quantification of target gene mRNA levels for the same strains is depicted in Figure S3J.