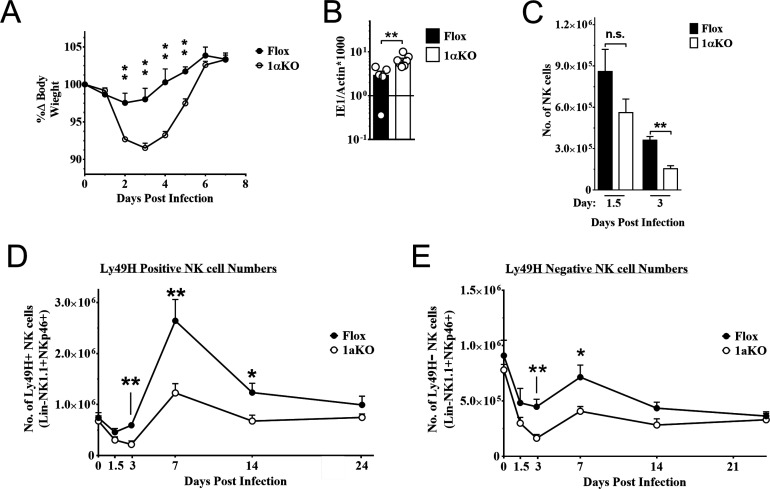
Figure 2. Natural killer (NK) cells require hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF1α) for an optimal response to virus infection.
(A) 1αKO or FL control mice were infected with 50K plaque forming unit (pfu) then monitored for weight loss over 7 days. Each data represents four mice from two independent experiments. (B) Splenic viral load in 1αKO or FL control mice were infected with 50K pfu then spleens harvested day 5 post-infection (pi). Data are pooled from four biologically independent experiments with a total of 5–7 mice in the indicated groups. (C) Number of bulk NK cells was quantified at days 1.5 and 3 pi from 1αKO or FL control mice. Data are from 2–3 independent experiments with 4–6 mice per group. (D) 1αKO or FL control mice were infected with 50K pfu and Ly49H+ NK cell expansion was determined at days 1.5, 3, 7, 14, and 24 pi. Data are from three independent experiments with 4–9 mice per group. (E) Quantification of 1αKO or Flox Ly49H- NK cells at days 1.5, 3, 7, 14, and 24 post murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) infection. Data are from 3–4 independent experiments with 3–4 mice per group. Data depict mean ± SEM, with each data set containing data indicated number of mice per group from independent experiments. Unpaired t-test was performed on (A–D). Statistical significance indicated by n.s., no significant difference; *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001.