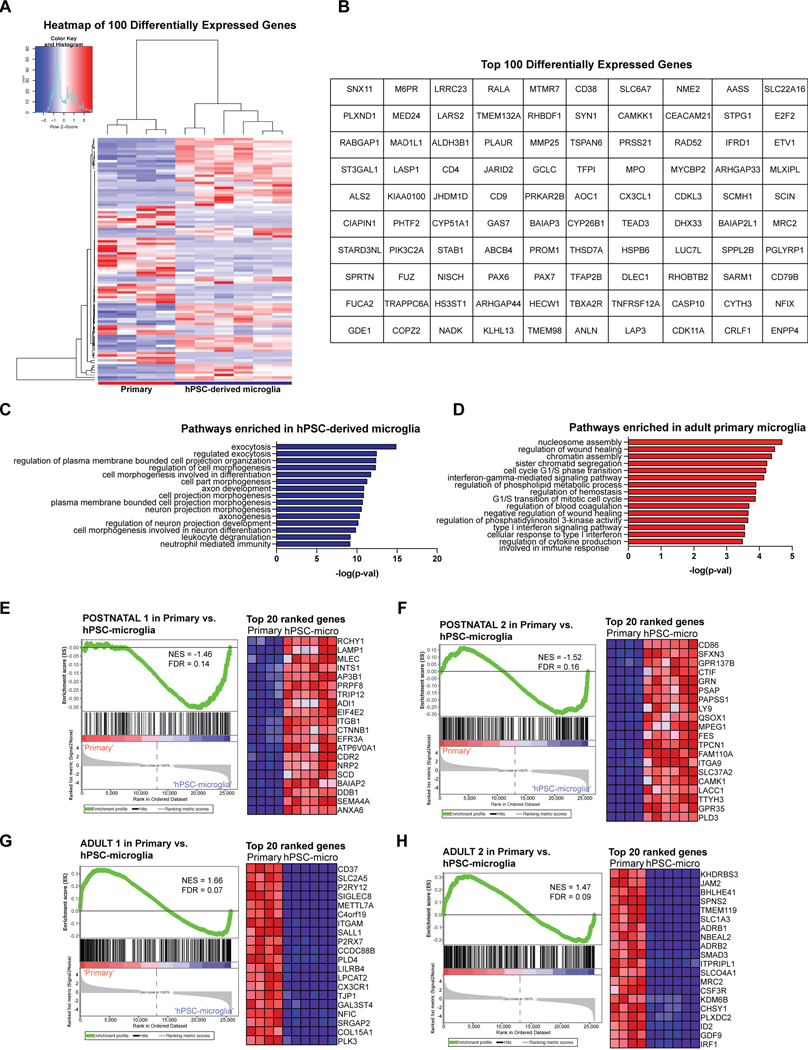
Extended Data Fig. 5. GO pathway analysis and GSEA on differentially expressed genes between hPSC-derived microglia and acutely isolated adult primary microglia.
A) Heatmap of top 100 differentially expressed genes between hPSC-derived microglia derived from method ii and acutely isolated adult primary microglia using DESEQ. B) Table of top 100 differentially expressed genes between hPSC-derived microglia (method ii) and adult primary microglia using DESEQ. C) GO pathway analysis identifies neuronal developmental pathways as enriched in hPSC-derived microglia (method ii). D) GO pathways analysis identifies immune activation pathways as enriched in acutely isolated adult primary microglia. E-F) GSEA on 7 embryonic to adult microglial gene signatures33 (yolk sac, embryonic 1 and 2, postnatal 1 and 2, adult 1 and 2) reveals that hPSC-derived microglia (method ii) enrich for postnatal 1 and 2 signatures with NES = −1.46 and FDR = 0.14; NES = −1.52, FDR = 0.16. G-H) GSEA reveals that adult primary microglia enrich for adult 1 and 2 signatures with NES = −1.52 and FDR = 0.16; NES = −1.47, FDR = 0.09. Heatmaps show top 20 ranked genes from each gene signature in primary vs. hPSC-microglia (method ii).