Fig. 2:
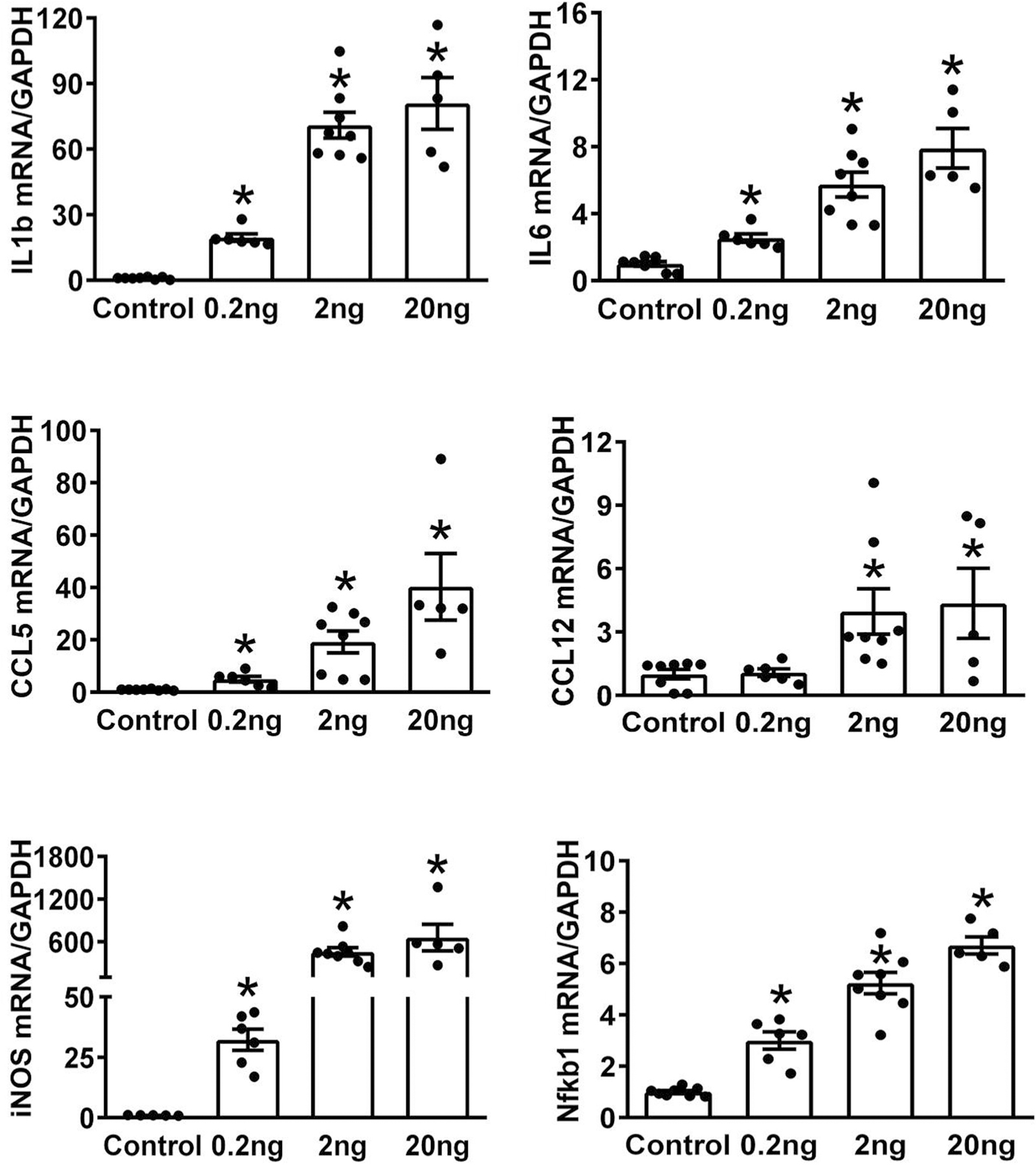
Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNFα) treatment results in a dose-dependent increase in mRNA expression of inflammatory mediators in brain neurons of neonatal Sprague Dawley (SD) rats. Neuronal cells were obtained from the cortex, hippocampus, and hypothalamus and were treated with differing doses of TNFα (0.2 ng/mL, 2 ng/ml, and 20 ng/ml) for 6 h. Cells were collected and mRNA levels of inflammatory mediators were measured using real time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Each treatment using 2~3 well of neuronal cells, and each experiment was repeated using 3 different batch of cells, the results were combined. Data were normalized to the housekeeping gene, GAPDH (n=6~9/group, *P<0.05)
