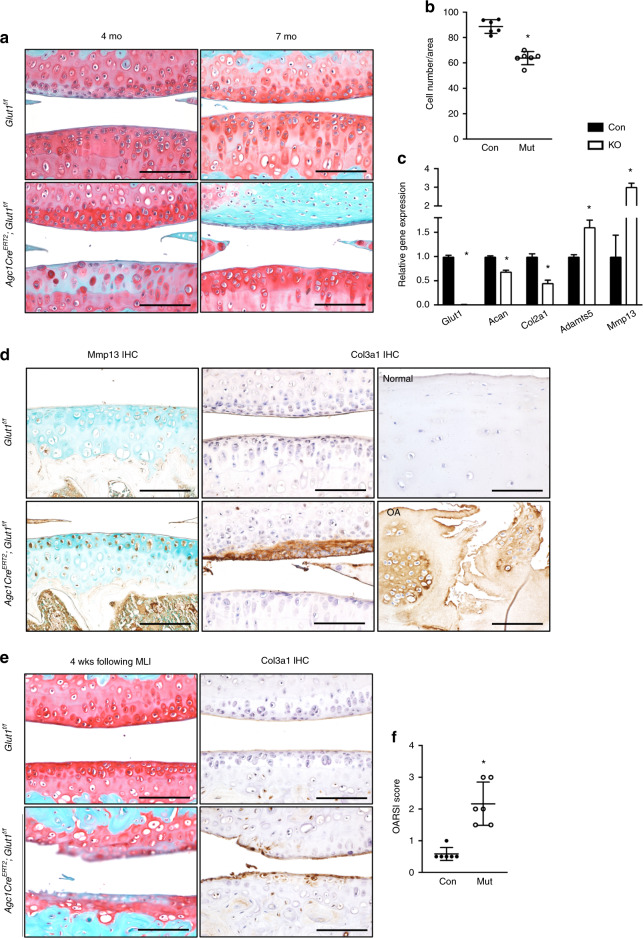
Fig. 4.
Deletion of Glut1 in chondrocytes decreases cellularity, disrupts cellular homeostasis, and ultimately causes cartilage fibrosis in AC. a Safranin O/Fast Green staining of knee sections of control and Glut1 LOF mice at 4 months and 7 months. N = 6. Scale bar, 100 μm. b Histomorphometric analyses of chondrocyte numbers in knee sections at 4 months. The data are the mean ± SD. N = 6. *P < 0.05. c RT-qPCR analyses for Glut1, Col2a1, Acan, Adamts5 and Mmp13 in control and Glut1 KO primary AC chondrocytes. All mRNA abundances were normalized to that of β-actin and then normalized to those of the controls. The data are the mean ± SD. N = 3. *P < 0.05 relative to the controls. d Immunostaining for Mmp13 and Col3a1 in knee sections of control and Glut1 LOF mice at 4 months (N = 6) or of Col3a1 in biopsies of normal and osteoarthritic cartilage from human patients (N = 3). Scale bar, 100 μm. e Safranin O/Fast Green staining and Col3a1 immunostaining of knee sections of control and Glut1 LOF mice at 4 weeks following MLI injury. N = 6. Scale bar, 100 μm. f OARSI scores for the medial tibial plateau and femoral condyle at 4 weeks following MLI injury. The data are the mean ± SD. N = 6. *P < 0.05 compared to the controls