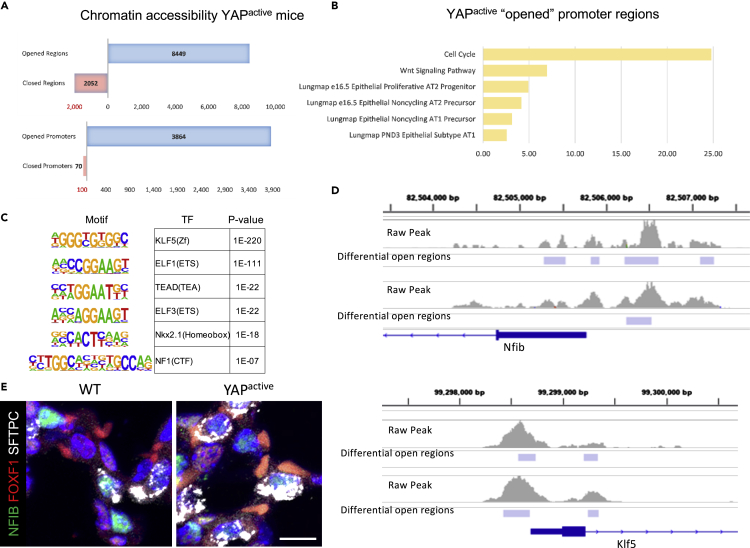
Figure 7.
YAP regulates chromatin accessibility of promoter regions in genes associated with alveolar differentiation
ATAC-seq was performed on EPCAM+ cells isolated from PND14 YAPactive (N = 3) and WT (N = 3) mice.
(A) YAP activation opened over 8400 regions of DNA and closed 2052 regions (p < .01). Over 3800 gene promoters (1.5kb of predicted transcriptional start site) were opened in YAPactive epithelial cells with only 70 promoters being closed.
(B) Functional enrichment analyses of genes with opened promoters opened in YAPactive mice show increased accessibility of signature genes for various AT1 and AT2 subtypes along with genes involved in Wnt signaling and cell cycle.
(C) Motif enrichment analyses of the regions opened in YAPactive mice show an enrichment for multiple transcription factors that were predicted regulators of the AT1 and/or AT2 cell TRN.
(D) IGV was used to visualize regions opened in Nfib and Klf5 promoter regions in YAPactive epithelial cells. ATAC-seq analyses were done using Mac2 on 2 litters, with YAPactive (N = 3) compared to Stk3flox/floxStk4flox/flox (N = 3) control littermates. Only regions altered in both litters were considered significant.
(E) Immunofluorescence analysis of NFIB (green), FOXF1 (red), and SFTPC (white) demonstrates NFIB in a subset of SFTPC+ cells in both WT and YAPactive mouse lungs. See Figure S3 for analysis of ATAC-seq quality.