Figure 3.
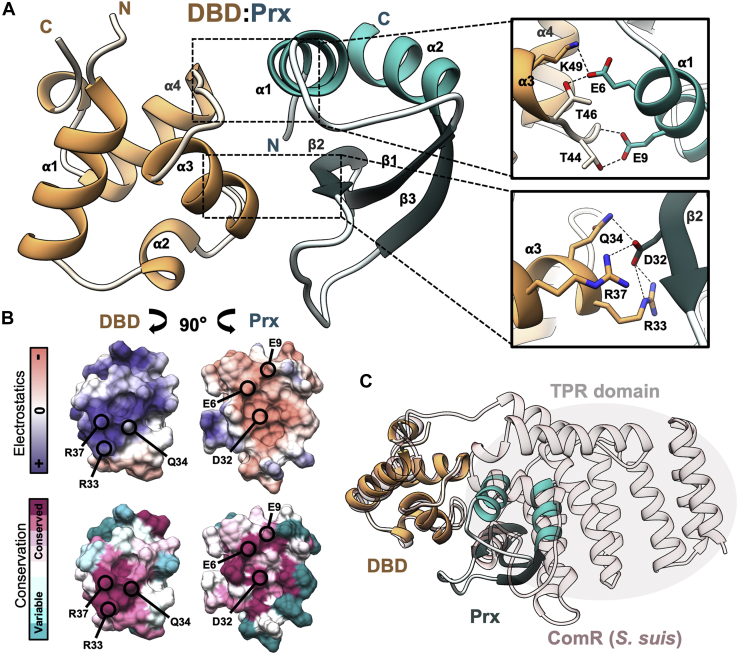
Cocrystal complex of Prx and the DNA-binding domain of ComR.A, cocrystal complex of the minimal ComR DBD (orange) with Prx (cyan). Inset boxes demonstrate key hydrogen-bond and salt-bridge interactions (dashed lines) between conserved residues in Prx and the residues in the DBD. The chosen residues in the DBD are critical for recognizing DNA and stabilizing the inactive apo-ComR conformation. Secondary structures are labeled by alpha-helix (⍺) and beta-strand (β) with the N-terminus and C-terminus labeled for each protein. B, molecular surface representations showing the electrostatics (top) and residue conservation (bottom) of the DBD and of Prx. The represented views are the structures in panel A rotated an opposing 90 degrees to display the surfaces in each protein at the interaction face. Select residues from panel A are indicated. C, overlay of the DBD:Prx complex on the structure of full-length ComR from S. suis (light pink) (PDBid: 5FD4) aligned by the DBD showing a steric clash with the TPR.