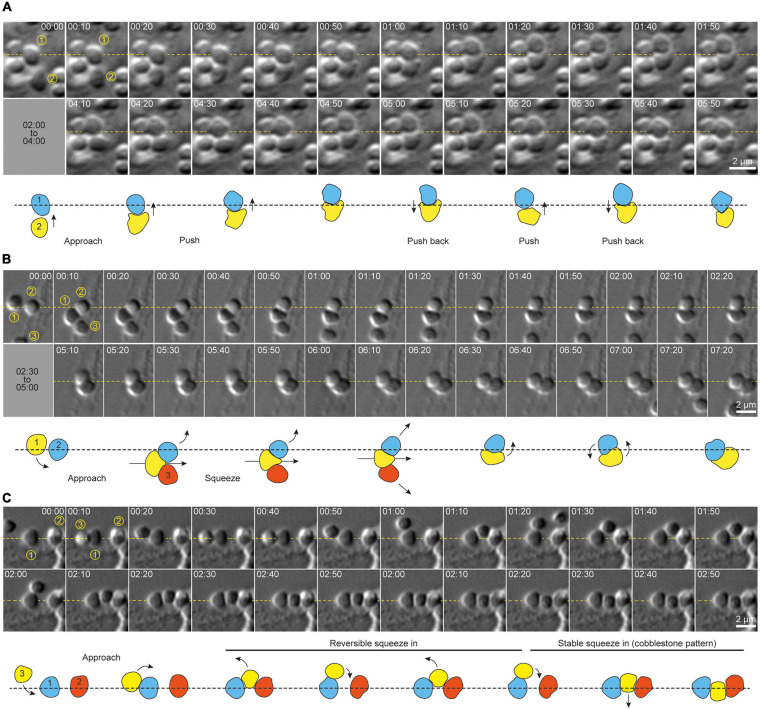
FIGURE 3.
Cell shape transitions underlie dynamic cell-cell interactions and social behavior in S. acidocaldarius. (A) Example of shape shifting in two cells interacting together. Shape transitions seem to accompany the production of force by each cell against the other. (B) Example of shape shifting in a cell (1) actively moving in between two other cells (2 and 3). Here again, shape shifting seems to occur along with the production of forces that push cells 2 and 3 aside. (C) Example of shape shifting in a cell (3) intercalating in between two pre-existing neighbor cells (1 and 2). Here, shape shifting seems reversible, as the cell 3 slides in and out of the gap between cells 1 and 2. Eventually cell 3 changes shape again to accommodate this space more stably, and form a cobblestone-like chain of cells with cells 1 and 2. DIC, 75°C, 100X + 1.5X lens. Interpretative diagrams are shown below each series of snapshots. Arrows show the direction of cell movements. Times are provided in min:sec.