Figure 4. TBK1 switches from a YAP1 complex to mTOR/S6K, facilitating LATS1-mediated YAP1 suppression.
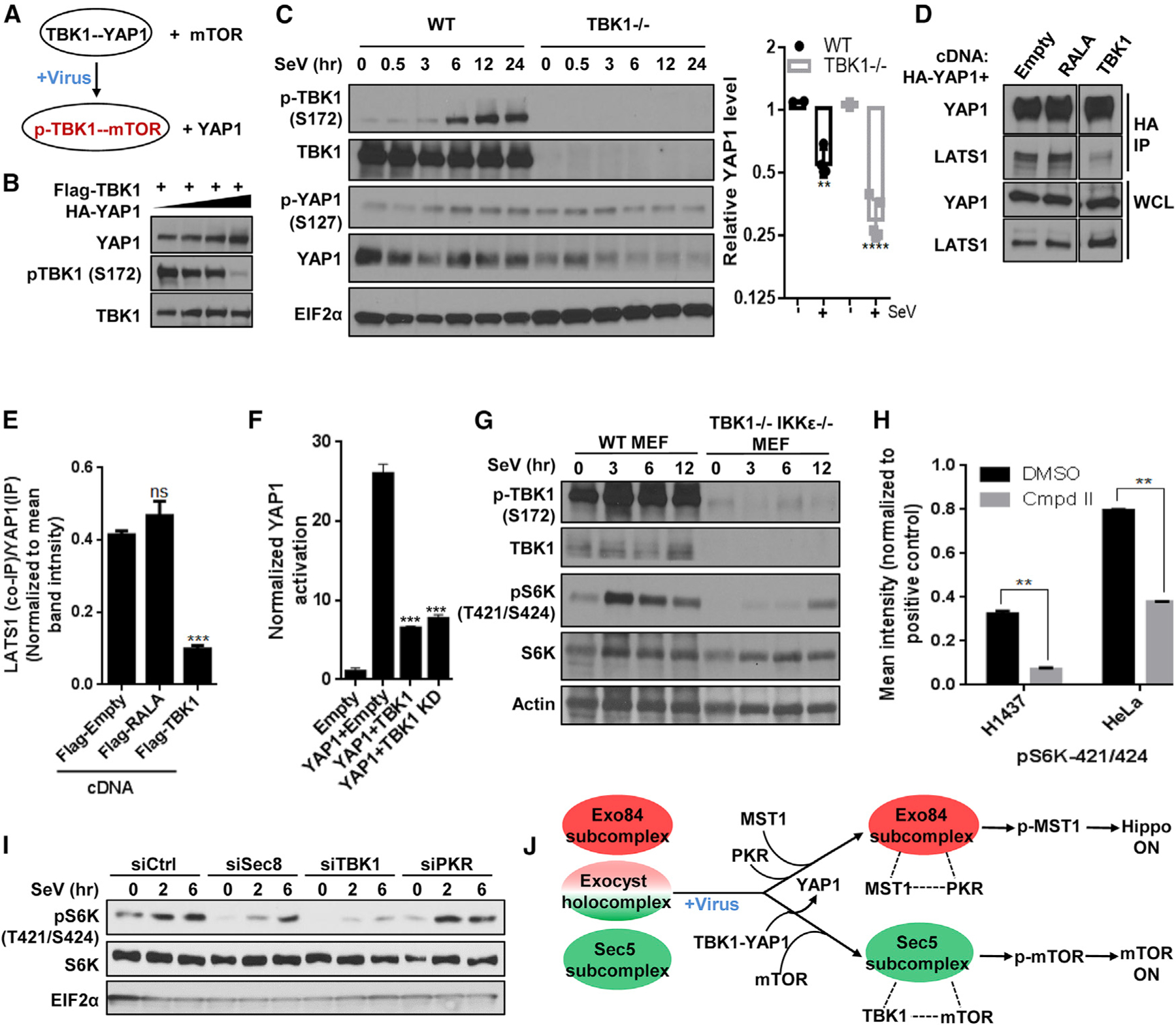
(A) Schematic diagram illustrating partner swapping event for TBK1 stable complex.
(B) YAP1 inhibits TBK1 activity. HEK293T cells expressing FLAG-TBK1 along with increasing amount of HA-YAP1 were grown and analyzed for western blot.
(C) TBK1 is protective for YAP1. (Left) TBK1 null and WT MEFs were incubated with SeV and analyzed using SDS-PAGE. (Right) YAP1 level for each time point was calculated by measuring individual band intensity. For comparison between WT and null cohort (as described in Figure 3B), unpaired t test p value was **p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001. Control WT cohorts were identical to the ones indicated in Figure 3B (n = 2).
(D and E) TBK1 competes with LATS1/2 for binding with YAP1. (D) Cells transiently expressing HA-YAP1 with or without plasmids co-expressing indicated cDNAs were grown to confluence, and YAP1 was affinity purified using an antibody against the HA tag and was analyzed for levels of indicated proteins using SDS-PAGE on the same gel. (E) Intensities of the bands were quantified and represented as mean ± SD in the bar graph (n = 2).
(F) TBK1 inhibits YAP1 activity. YAP reporter activity was measured in the presence of empty vector or the cDNAs indicated. Normalized fold change in Hippo signaling activation is represented as histograms representing mean ± SD. Statistical comparison between treatment cohorts was measured using a Student’s unpaired t test where p < 0.001 and n = 3.
(G) TBK1 regulates virus infection-induced S6K phosphorylation. Near-confluent culture of TBK1 WT and TBK1- and IKKε-deficient MEFs were incubated with 50 HAU/mL SeV. Lysates were collected and analyzed using SDS-PAGE (n = 2).
(H) Compound II, a specific TBK1 inhibitor, inhibits S6K phosphorylation on residues 421/424. Confluent cultures from eight cell lines from melanoma and lung cancer origin were treated with either DMSO or CmpdII (TBK1i/TBK1 inhibitor) for 30 min, and cells harvested were analyzed for phospho-protein level of 16 AKT pathway proteins by using phospho-ELISA array. Quantification of the phosphorylation of p70S6K in DMSO-versus CmpdII-treated H1437 and HeLa cell line samples in Figure S4E are represented as bar graph, and data are represented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was calculated using Mann-Whitney U test, where p < 0.01 (n = 2).
(I) The exocyst and TBK1 support virus challenge-induced S6K phosphorylation. HEK293T cells reverse transfected with indicated short interfering RNAs (siRNAs) were grown to confluence and incubated with SeV. Cell lysates were analyzed for S6K phosphorylation using SDS-PAGE (n = 2).
(J) Summary of the virus infection stimulus-specific regulatory interaction from TBK1’s orientation.
