FIGURE 1.
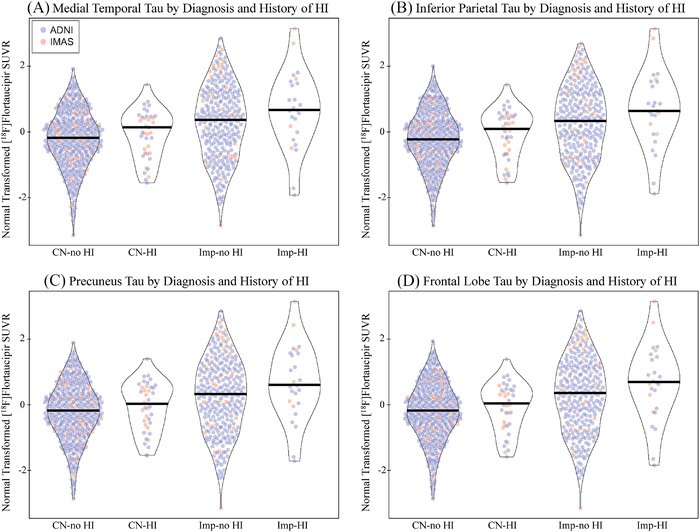
Tau deposition by diagnosis and history of head injury. Individuals with a history of head injury (HI) with or without a loss of consciousness (LOC) show greater normal transformed [18F]flortaucipir SUVR in the (A) medial temporal lobe (DX: P < .001, d = 0.313; HI: P = .034, d = 0.156; DX by HI: P > .1), (B) inferior parietal lobe (DX: P < .001, d = 0.307; HI: P = .024, d = 0.166; DX by HI: P > .1), (C) precuneus (DX: P < .001, d = 0.302; HI: P = .025, d = 0.165; DX by HI: P > .1), and (D) frontal lobe (DX: P < .001, d = 0.309; HI: P = .038, d = 0.153; DX by HI: P > .1). This effect appears to be driven by the impaired participants in the study. Age, sex, mean global amyloid, and race/ethnicity were included as covariates. Note: Participants include 412 CN without history of HI, 38 CN with history of HI, 277 impaired without history of HI, 25 impaired with history of head injury. Abbreviations: ADNI, Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative; CN, cognitively normal; d, Cohen's d; DX, diagnosis; HI, head injury; IMAS, Indiana Memory and Aging Study; LOC, loss of consciousness; SUVR, standardized uptake value ratio
