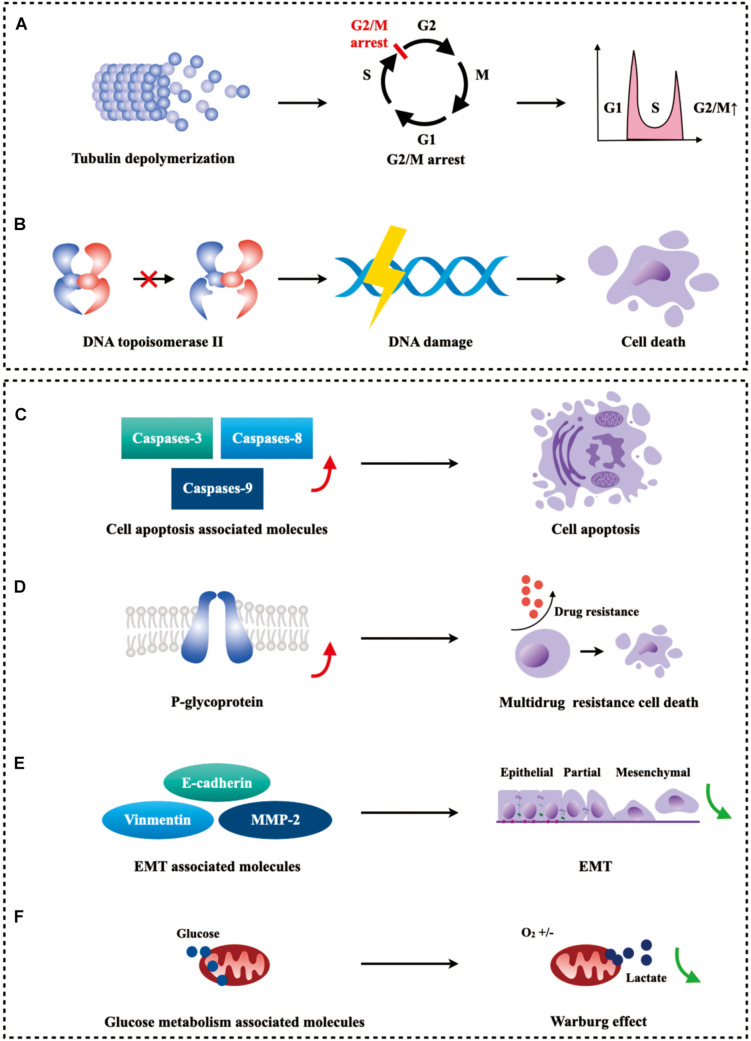
FIGURE 6.
Schematic diagram of the mechanism of PTOX derivatives for cancer treatment. (A) PTOX derivatives act as inhibitors of tubulin to induce G2/M arrest in tumor cells. (B) PTOX derivatives can inhibit the degradation of topoisomerase II to cause DNA damage and eventually trigger cell death. (C–F) PTOX derivatives can inhibit the growth of tumor cells by affecting drug-resistant tumor cells, apoptosis-related molecules, EMT-related molecules, and gluconeogenesis-related molecules, respectively.