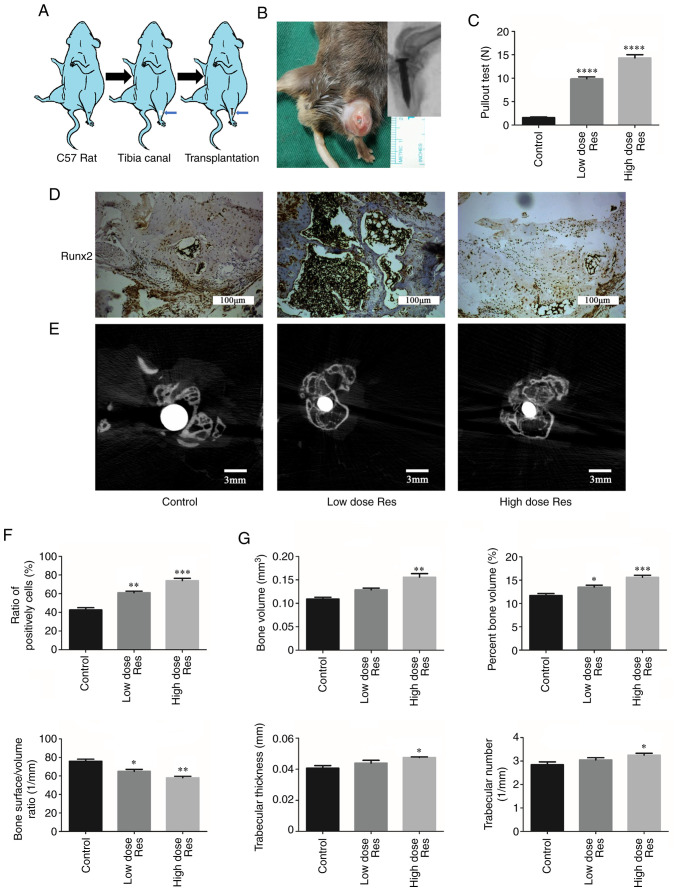
Figure 3.
Resveratrol enhances bone formation around the prosthesis in vivo. (A) Schematic drawing of the transplantation procedure. (B) Establishment of the model of aseptic loosening. (C) Pulling force required to remove the titanium pin implant from the tibia with or without resveratrol. (D-G) Immunohistochemistry and µCT were used to determine the effects of resveratrol on bone formation. (D and F) Immunohistochemical staining and semi-quantification of Runx2 protein expression levels in periprosthetic tissues. The ratios of the number of cells positively stained for Runx2 to the total number of cells were plotted. Scale bar, 100 µm. (E and G) Cross-sectional images of titanium implants and bone microstructure analyzed by µCT scans (Scale bar, 3 mm); the bone volume, percentage bone volume, bone surface density, trabecular thickness and trabecular number were calculated. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.001 vs. the control group (n=3). µCT, micro-CT; Res, resveratrol; Runx2, runt-related transcription factor 2.