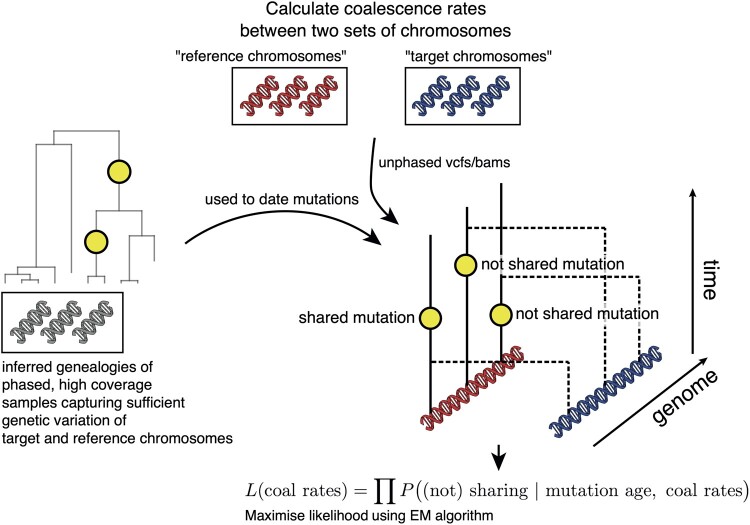
Fig. 1.
Colate calculates coalescence rates between two sets of chromosomes, labeled target and reference (main text). The method proceeds by recording for each mutation carried by a reference chromosome, whether it is shared in the target chromosomes. This information is summarized in a likelihood, constructed by multiplying over SNPs, such that no phase information is required. Whenever more than one chromosome is available at any given site, we multiply across chromosomes. The likelihood is maximized using an EM algorithm.