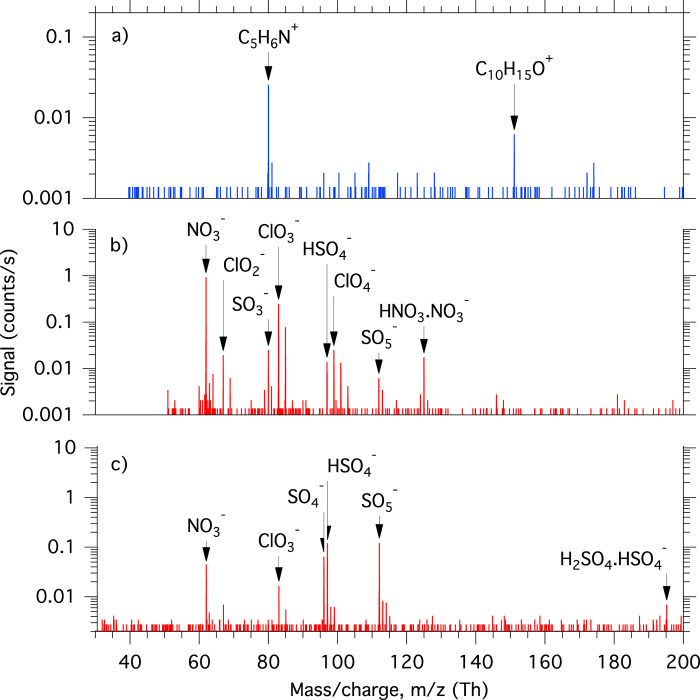
Extended Data Figure 1. Small-ion mass spectra.
a, b, Composition of positive (a) and negative (b) small ions measured by the APi-TOF under GCR conditions and before adding any SO2 to the chamber. The experimental conditions are zero α-pinene, 35 p.p.b.v. O3, zero H2 or HONO, 38% relative humidity, 278 K and [H2SO4] < 5 × 104 cm−3. Collisions will transfer positive charge to contaminant molecules having the highest proton affinity (a), and negative charge to contaminant molecules with the lowest proton affinity, that is, highest gas-phase acidity (b). From molecular cluster measurements, the positive ions also include ammonium (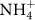 ), but its mass is below the set acceptance cut-off of the APi-TOF. c, The negative small-ion spectrum at [H2SO4] = 1.2 × 105 cm−3, after adding 32 p.p.t.v. SO2 to the chamber, showing that the dominant ions species shift from nitrate to sulfur-containing. The experimental conditions are 340 p.p.t.v. α-pinene, 35 p.p.b.v. O3, zero H2 or HONO, 38% relative humidity and 278 K. Water molecules evaporate rapidly from most hydrated ions in the APi-TOF and so are not detected.
), but its mass is below the set acceptance cut-off of the APi-TOF. c, The negative small-ion spectrum at [H2SO4] = 1.2 × 105 cm−3, after adding 32 p.p.t.v. SO2 to the chamber, showing that the dominant ions species shift from nitrate to sulfur-containing. The experimental conditions are 340 p.p.t.v. α-pinene, 35 p.p.b.v. O3, zero H2 or HONO, 38% relative humidity and 278 K. Water molecules evaporate rapidly from most hydrated ions in the APi-TOF and so are not detected.