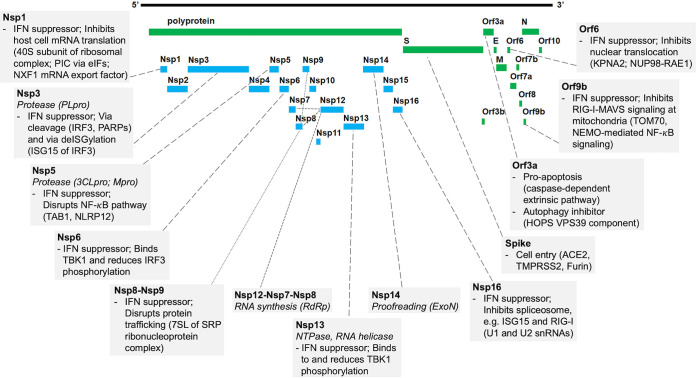
FIG 1.
SARS-CoV-2 protein functions and host interactions. Shown is a graphic representation of the SARS-CoV-2 proteome. Boxes connected to proteins indicate the virus transcription and translation functions (italics) (summary of Table 1) and known human protein interaction with their effect on human pathways (summary of Table 2). Abbreviations: 3CLpro, 3-chymotrypsin-like protease; 7SL, RNA component of SRP ribonucleoprotein complex; ACE2, angiotensin I-converting enzyme 2; eIFs, eukaryotic translation initiation factors; ExoN, exoribonuclease; HOPS, homotypic fusion and protein sorting complex; IFN, interferon; IRF3, interferon regulatory factor 3; ISG, interferon-stimulated gene; KPNA2, karyopherin alpha 2; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein; Mpro, main protease; NEMO, NF-κB essential modulator; NLRP12, NLR family pyrin domain containing 12; NUP98, nuclear pore complex protein 98; NXF1, nuclear RNA export factor 1; PARPs, poly(ADP-ribosyl) polymerases; PIC, ribosomal preinitiation complex; PLpro, papain-like protease; RAE1, RNA export 1; RdRp, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; RIG-I, retinoic acid-inducible gene I; SRP, signal recognition particle; TAB1, TGF-β-activated kinase 1 (MAP3K7) binding protein 1; TBK1, TANK binding kinase 1; TMPRSS2, transmembrane serine protease 2; TOM70, translocase of outer membrane 70 (subunit of mitochondrial import receptor); VPS39, vacuolar protein sorting 39 (subunit of HOPS complex).