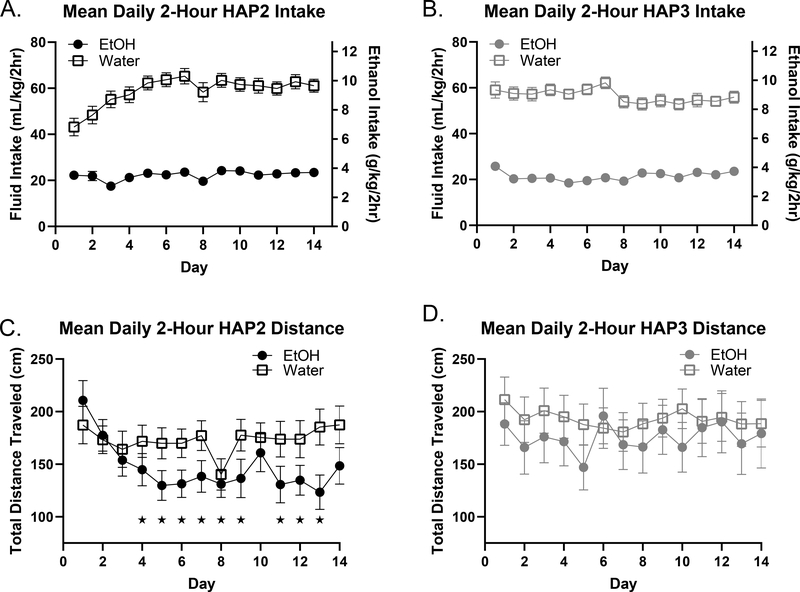
Figure 1. Mean Daily Intake and Distance Travelled Over Two Weeks.
Intake: In both replicates, the water group consumed more total fluid each day during DID than the EtOH group, [post-hoc analysis following up on a main effect of group; p < 0.05]. We also note that EtOH intake in both replicates was reliable such that all animals readily consumed pharmacologically relevant (binge) levels of EtOH every day. Error bars are sometimes obscured by the plot symbols (A, B). Distance: In HAP2 mice, a day*group interaction is driven by initial greater locomotor activity in the EtOH group rapidly declining at a much faster rate than the water group whose activity stabilizes around day 3 (C). In HAP3, no significant effects were observed, indicating similar levels of activity between EtOH and water consuming animals in this replicate (D). Multiple comparison tests were conducted wherein distance travelled on each day within a given fluid group (EtOH or Water) was compared to day 1. Results indicate significant differences in the HAP2 replicate only, where days which differed from day 1 are indicated with *. These results indicate the potential of EtOH-induced locomotor sedation in HAP2 mice only.