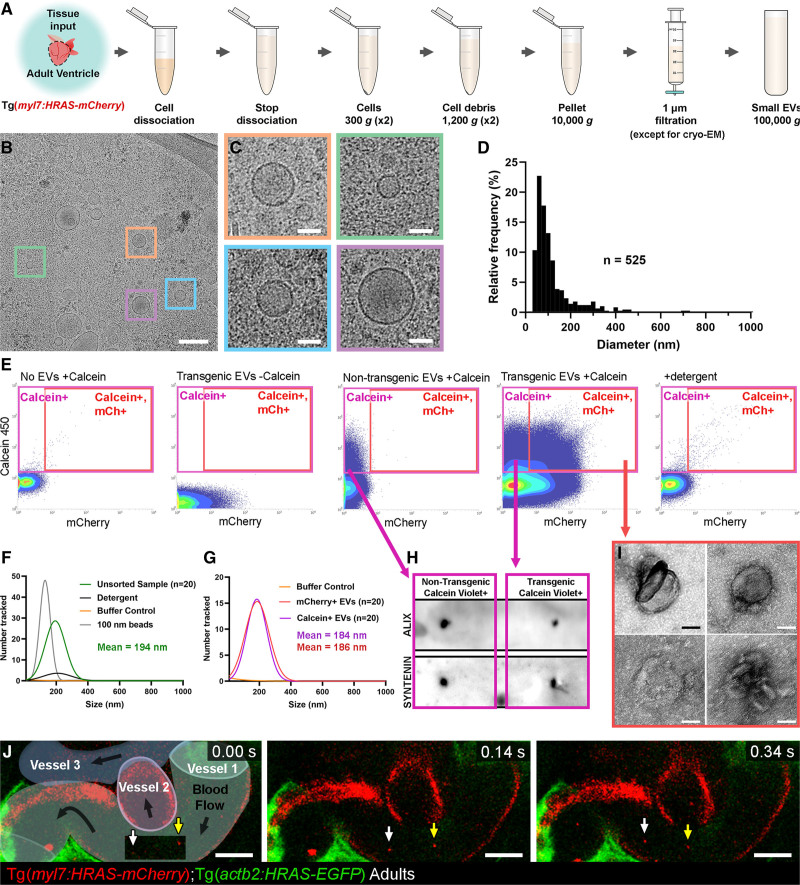
Figure 4.
Validation of endogenous cardiovascular extracellular vesicles (EVs) from adult zebrafish.A, Schematic describing the centrifugation steps taken to isolate EV fractions following cell dissociation of adult zebrafish ventricular tissue. B and C, Cryo-EM micrograph of isolated EVs from a pool of ventricles (n=60). C, A panel of 4 higher magnification views of the boxed regions in B. D, Histogram of the size distribution of EVs visualized by cryo-EM. n refers to number of EVs analyzed. E, Typical flow cytometry scatter plots showing the gates used to sort adult cardiac EVs and the controls used to define these gates. F and G, Gaussian distribution of NTA analysis on unsorted EV fractions before and after detergent treatment (F) and after sorting for calcein+ EVs and mCherry+ calcein+ EVs (G). H, Dot blot analysis of protein extracted from FAVS isolated particles, sorted for calcein+ EVs from both nontransgenic and Tg(myl7:HRAS-mCherry) adult ventricular tissue, confirms expression of the EV components Alix and Syntenin. I, TEM-negative stain micrographs of FAVS isolated particles, sorted for mCherry+ calcein+ EVs from Tg(myl7:HRAS-mCherry) adult ventricular tissue. J, Schematic overlay describing the position of the 3 vessels visible in the integrated time series of live imaging of endothelial cell-EVs in the peripheral circulation of an adult Tg(actb2:HRAS-EGFP); Tg(kdrl:mCherry-CAAX) double transgenic fish. White and yellow arrows indicate 2 EC-EVs moving with the blood flow. Scale bars: B, 200 nm; C and I, 50 nm; J, 10 μm.