FIG 5.
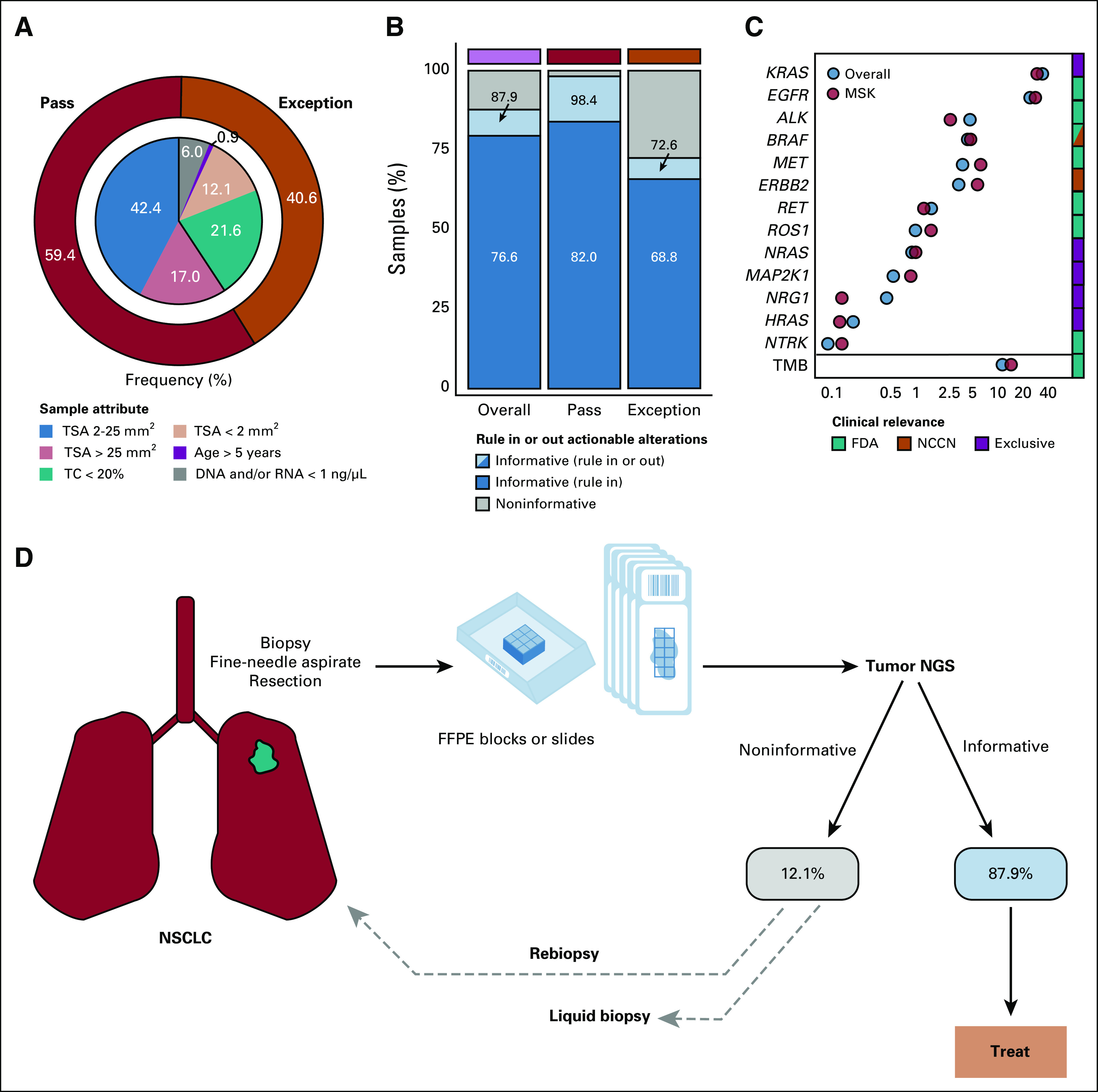
(A) Donut plot characterizing the composition of consecutively tested, sample input characteristic-evaluable NSCLC adenocarcinoma samples (n = 1,142) from the overall PCR-CGP test cohort. The outer ring indicates the percentage of samples meeting (pass: dark red) or not meeting (exception: orange) PCR-CGP input requirements. In the inner pie chart, samples passing all input requirements are stratified by TSA; exception samples are stratified by indicated sample attribute (TC < 20%; TSA < 2 mm2; age > 5 years: specimen collected > 5 years before PCR-CGP; and DNA and/or RNA concentration < 1 ng/µL). (B) The proportion of tested samples (overall and by sample input requirement category) for which an informative result (able to rule in or out actionable alterations) was reported. To be considered informative, the test must have either reported a therapy selection and/or mutually exclusive biomarker (as in C and the Data Supplement) or tested definitively negative for all such biomarkers by meeting all sequencing QC metrics and having TC ≥ 20% (the PCR-CGP test's overall limit of detection). (C) Reported actionable biomarker frequencies from this PCR-CGP NSCLC adenocarcinoma cohort (overall) are shown along with those from an external single-institution cohort (MSK-IMPACT; MSK: light red). The color bar at right indicates whether testing positive for each corresponding biomarker is associated with an FDA-approved (green) or NCCN-recommended (orange) targeted therapy or thought to be mutually exclusive (purple) with known LUAD therapy selection biomarkers. TMB frequencies are presented separately from gene-specific biomarkers given the expected overlap between TMB-high and some therapy selection or actionable biomarkers (for this analysis, samples with more than one biomarker were counted in each group). (D) Potential real-world NSCLC adenocarcinoma testing paradigm on the basis of sample characteristics and PCR-CGP performance characteristics observed in this cohort. Patients with noninformative test results in this cohort were not followed to determine whether rebiopsy or liquid biopsy testing was pursued. CGP, comprehensive genomic profiling; FDA, US Food and Drug Administration; FFPE, formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded; LUAD, lung adenocarcinoma; MSK, Memorial Sloan Kettering; NCCN, National Comprehensive Cancer Network; NGS, next-generation sequencing; NSCLC, non–small-cell lung cancer; PCR-CGP, multiplex polymerase chain reaction–based comprehensive genomic profiling; QC, quality control; TC, tumor content; TMB, tumor mutation burden; TSA, tumor surface area.
