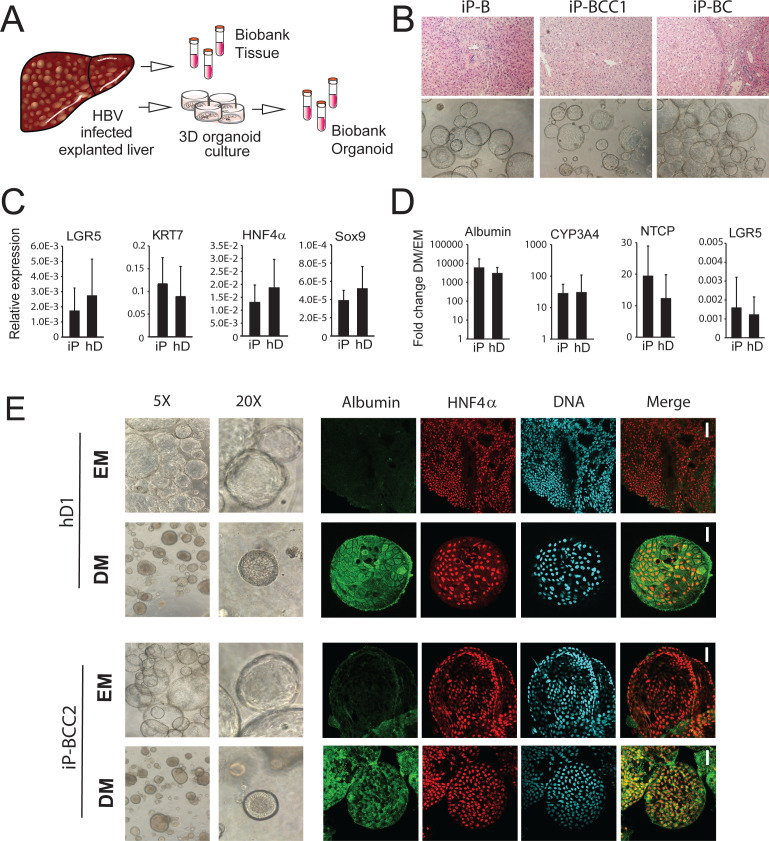
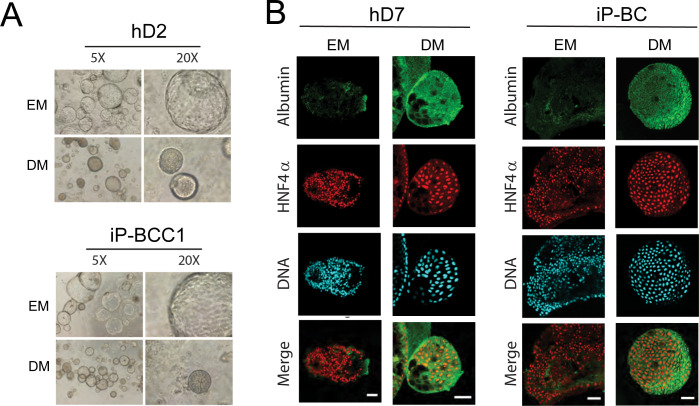
Figure 4. Characterization of organoid cultures from liver explants of HBV-infected patients.
(A) Representative panel showing the procedure to generate organoid cultures or biobanks from liver tissue. (B) Hematoxylin-eosin-stained sections of explanted liver tissue and phase-contrast pictures showing the morphology of liver organoids derived from hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infected individuals. (C) Expression profile of the progenitor markers LGR5, KRT7, HNF4α, and Sox9 in EM (undifferentiated) organoids derived from liver of healthy donors (hD) (n = 4) and HBV-infected individuals (iP) (n = 5). Levels of expression were calculated according to the 2ΔCT method using GAPDH as the reference gene. (D) Differentiation capacity of organoid cultures derived from liver of hDs (n = 4) and iPs (n = 5). Bars represent the fold difference in the expression of hepatocyte-specific genes encoding albumin, cytochrome CYP3A4, and sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide (NTCP), and the progenitor-specific gene LGR5 in DM (differentiated) cultures compared to EM organoids using the 2ΔΔCT method. (E) Immunofluorescent staining targeting albumin (green) and HNF4α (red) was performed in EM and DM organoids. Phase-contrast images, depicting the morphology of the cells, are shown as reference.