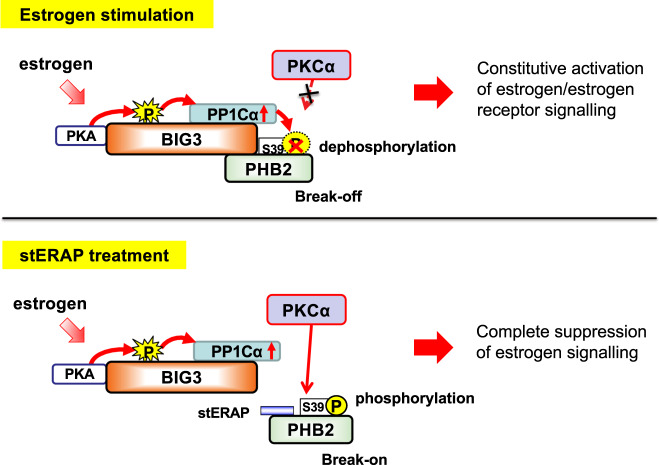
Fig. 3.
Pathophysiological role of the BIG3-PHB2 complex in estrogen-dependent breast cancer cells. Estrogen (E2) stimulation induces PKA-dependent BIG3 phosphorylation, which cancels its negative regulation of PP1Cα activity, resulting in the avoidance of PHB2 suppressive activity (Upper panel). stERAP competitively binds to endogenous PHB2, thereby preventing its interactions with BIG3. Free PHB2 directly binds to both nuclear and plasma membrane-associated ERα, resulting in repression of E2-induced genomic and non-genomic ERα activation (Lower panel)