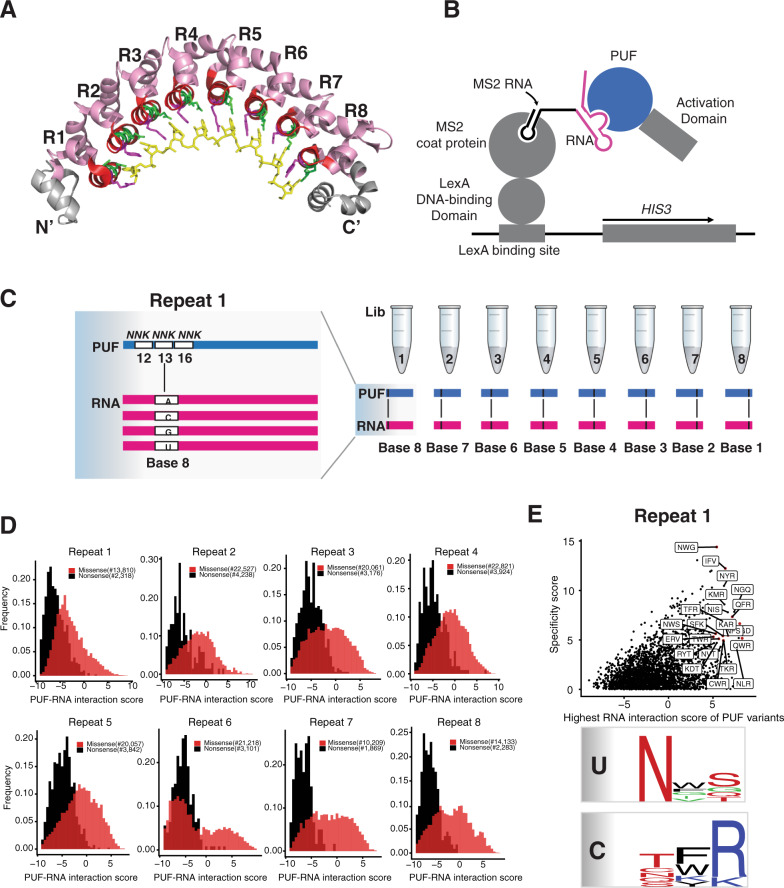
Fig. 1. A high throughput yeast three-hybrid assay to identify PUF variants.
A Crystal structure of the human Pumilio-1 PUF domain in complex with NRE10 RNA (PDB ID 1M8Y)26. Helices that carry functional RNA-binding residues (TRM residues) are colored in green and purple. TRM residues 12 and 16 are in green and position 13 is in purple. The RNA bases of the NRE10 recognition sequence are colored in yellow. B The yeast three-hybrid system was adapted for deep mutational scanning of the Pumilio-1 PUF domain TRM residues. Binding of the Pumilio-1 PUF domain to its cognate RNA sequence leads to the formation of a functional transcription factor that induces the expression of the reporter gene, HIS3. As a result, yeast cells that carry functional PUF-RNA interactions proliferate in media lacking histidine, while yeast cells that carry non-functional PUF-RNA interactions will be eliminated. C Workflow to analyze all possible TRM combinations (~8000) against the four possible RNA bases for each PUF repeat through deep mutational scanning. The left panel is shown as randomization of Repeat 1 and Base 8. D The frequency distribution of nonsense and missense PUF variants for all repeat locations. The X-axis is a measure of PUF-RNA interaction score. Black indicates nonsense variants and red indicates missense variants. E A plot showing the RNA interaction score and specificity score of each PUF variant in repeat 1. The X-axis indicates the highest RNA interaction score of each PUF variant. The Y-axis indicates the specificity score for each PUF variant. Each dot indicates one PUF variant and the red dot highlights those PUF variants with interaction score >5 and specificity score >4. The lower panel summarizes the base-specific recognition pattern for uracil and cytosine through sequence logos.