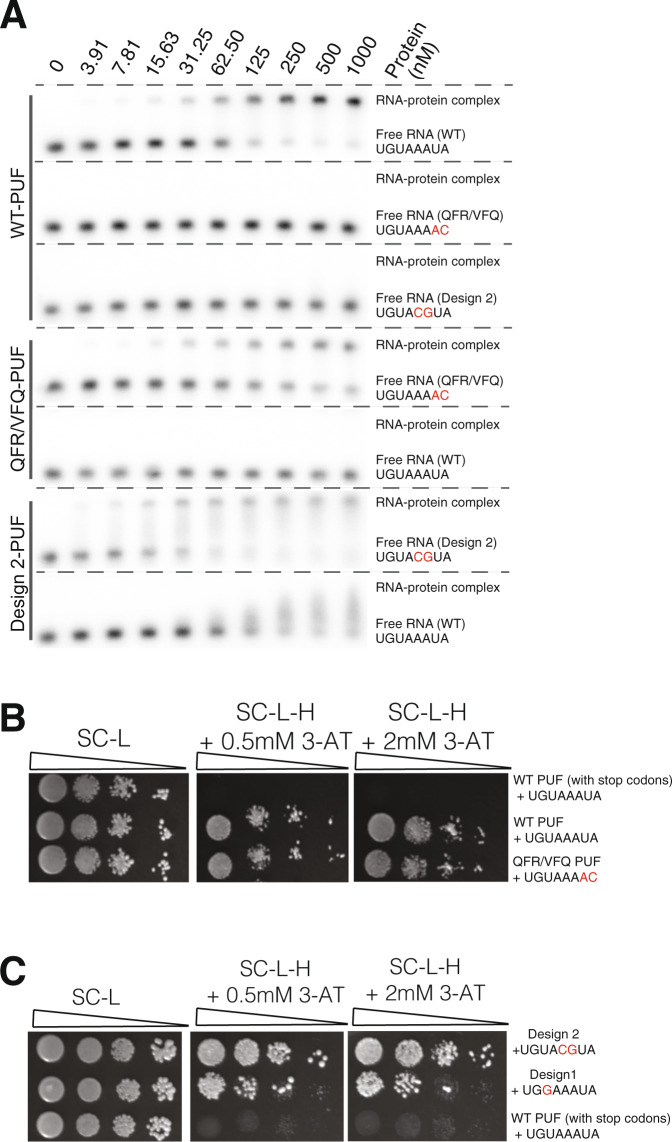
Fig. 7. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays and three-hybrid assays for wild-type and variant PUF domains.
A Electrophoretic mobility shift assays show the in vitro binding for the wild-type PUF domain, the QFR/VFQ PUF variant, and the design 2 variant to the wild-type RNA sequence or an RNA containing mutated bases. Results are representative of two biological replicates. B Yeast three-hybrid assays show the binding of the wild-type PUF domain and QFR/VFQ variant. The negative control is a wild-type PUF domain that has stop codons in the TRM locations (repeat 1) paired with wild-type RNA. SC-L, synthetic complete media minus leucine; SC-L-H, synthetic complete media minus leucine and histidine. C Spot dilution plate assay indicates the binding of the design 1 and design 2 PUF domains to their target RNAs. The negative control is as in (B). The starting OD600 that was spotted was 0.05, with three sequential 10-fold serial dilutions shown.