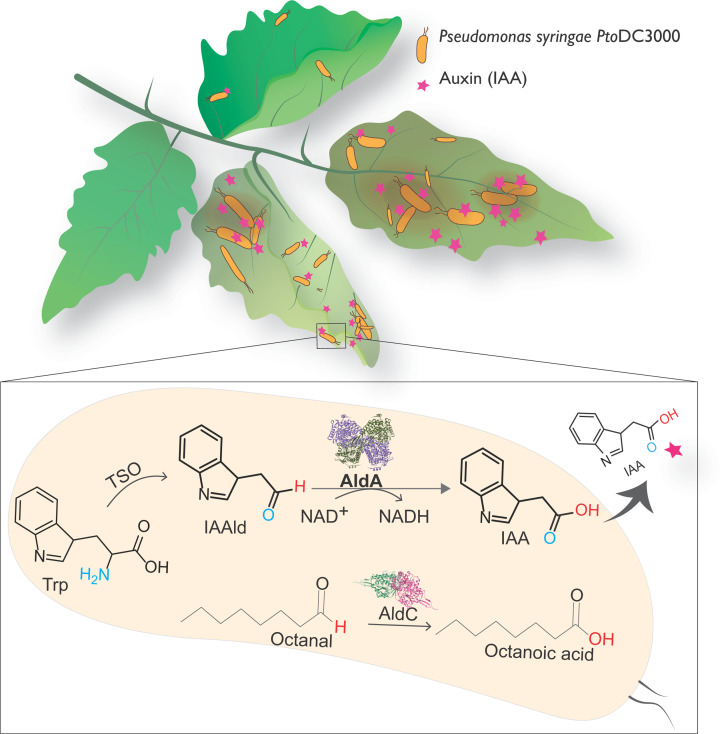
Figure 2. Plant pathogen P. syringae pv. tomato strain DC3000 synthesizes the auxin IAA, a plant growth hormone that facilitates its entry into the growing plant, and causing wilting and discoloration of the infected parts.
AldA is an IAAld dehydrogenase in P. syringae DC3000 which catalyzes the oxidation of IAAld to IAA coupled with reduction of NAD+ cofactor. Please refer to Figure 1 from Zhang et al. (2020) [33] for the detailed mechanism. AldC, another ALDH found in P. syringae oxidizes a range of long-chain aliphatic aldehydes such as octanal to the corresponding acids. Such aliphatic molecules have been hypothesized to assist microbes in gaining entry into the host cell and also to act as nutrients for their proliferation [32,34].