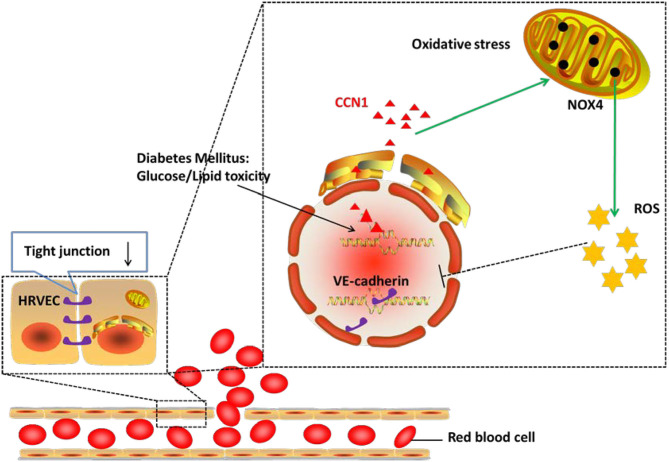
Figure 7.
Mechanism of action of CCN1 in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy (DR). The abnormal increase in CCN1 results from either the lipotoxicity or glucotoxicity of diabetes mellitus and leads to upregulated NOX4/ROS production, which further inhibits the expression of the tight junction protein.