FIGURE 1.
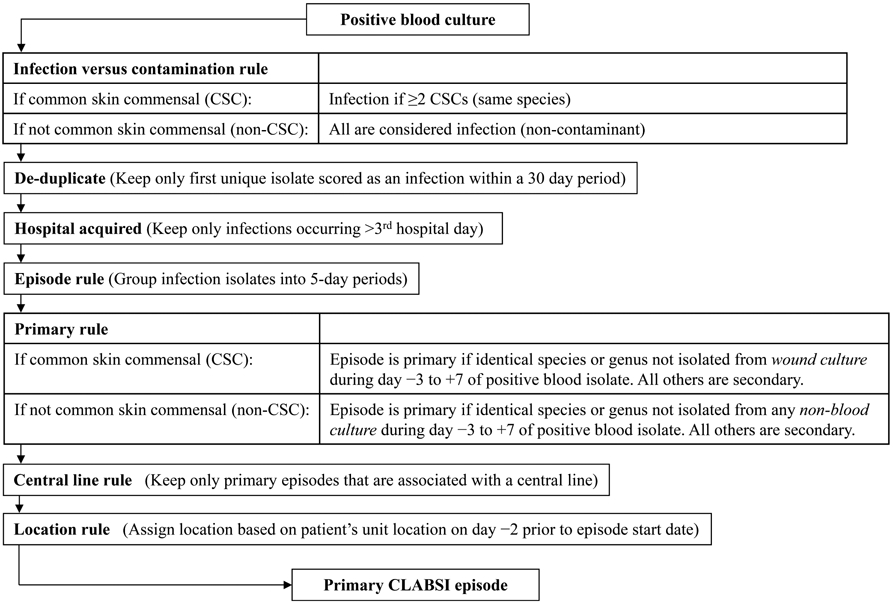
Schematic of computer algorithm adapting National Healthcare Safety Network criteria for central line–associated bloodstream infection (CLABSI) surveillance. Common skin commensals (CSCs) are defined as diphtheroids, Bacillus species, Propionibacterium species, coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species, or Micrococcus species. The computer algorithm required recovery of the same common skin commensal from 2 separate blood cultures within 2 consecutive hospital days in an episode. Calendar date of admission to the hospital is considered hospital day 1. Active surveillance screening cultures and catheter tip cultures were not considered to avoid misclassifying episodes as secondary. Central line presence included any duration of use and was assessed on first day of a primary bloodstream infection episode through 2 hospital days before the episode.
