Figure 2.
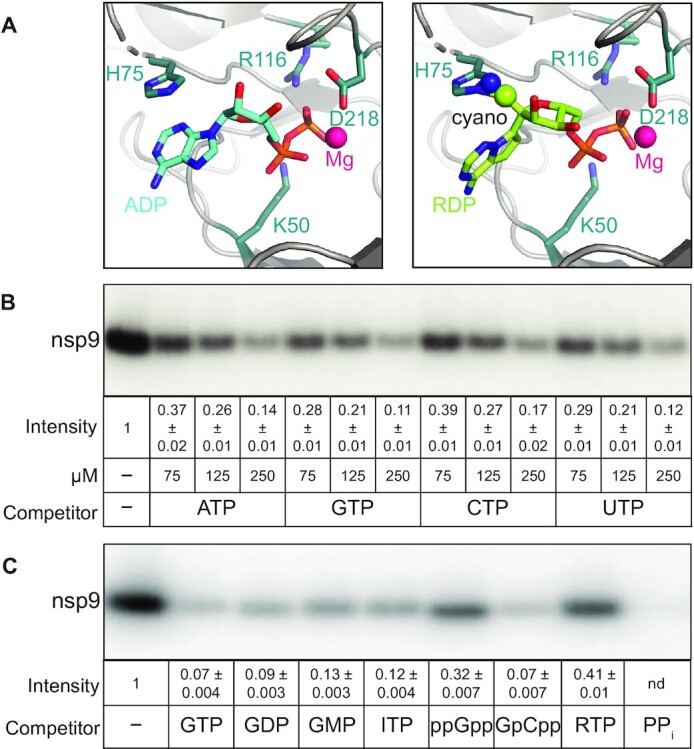
Effects of nucleotides on nsp9 modification. (A) Nucleotide binding to the NiRAN active site. The Mg2+ ion is shown as magenta sphere and key NiRAN residues - as sticks. Left, ADP (cyan carbon atoms) from PDB:6XEZ. Right, RDP (lime carbon atoms) modeled in place of ADP; the C1′ cyano group of RDP could clash with the side chain of nsp12 His75. (B) Unlabeled natural NTPs compete with [α32P]-GTP for transfer to nsp9. (C) GTP analogs and PPi inhibit NMPylation, but ppGpp and RTP do so less effectively; all nucleotides were present at 0.5 mM. In (B) and (C), NMPylation efficiency was compared to that observed in the absence of competitors, set at 1, and is shown as mean ± SD (n = 3).
