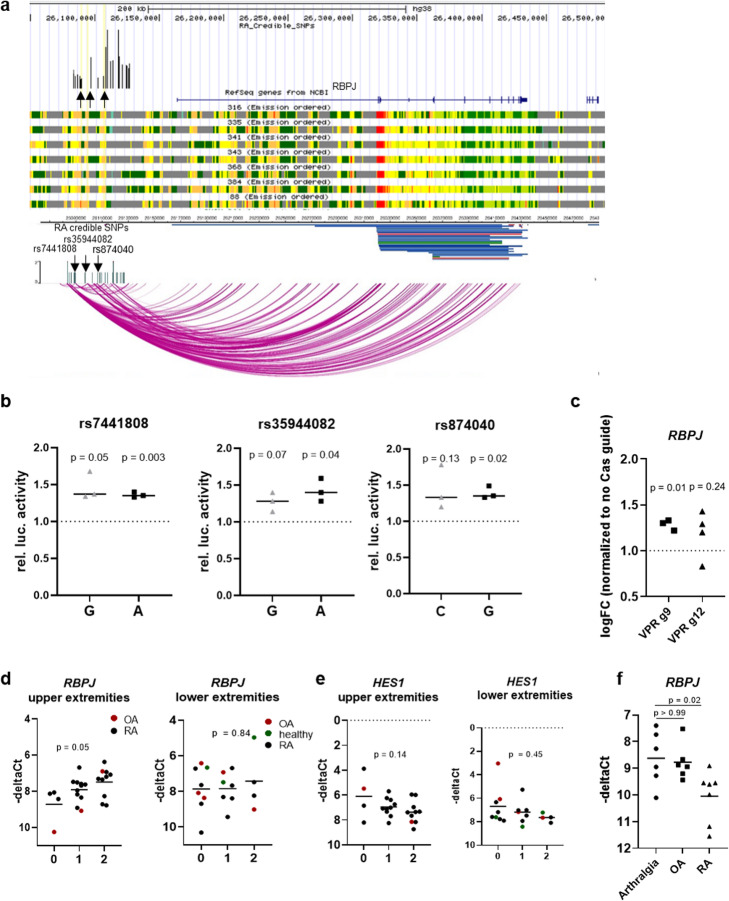
Fig. 7.
RBPJ expression in FLS is affected by genotype and disease. a Fine mapping, epigenetic and chromatin conformation analyses at the RBPJ locus. Black arrows indicate rs7441808, rs35944082, and rs874040, which were selected for further analysis. b Luciferase reporter assays showing relative enhancer activity of oligonucleotides containing risk (gray) and wild-type variants (black) of rs7441808, rs35944082, and rs874040 compared to empty vectors (set to 1). One sample t test. c RBPJ expression in FLS transduced with VP64-p65-Rta dCas9 (VPR) and two different guide RNAs (g9 and g12) targeting the genomic region around chr4:26106575 (rs87040). RBPJ expression was normalized to FLS that were transduced with respective guide RNAs but not VPR-dCas9 (set to 1). –deltaCt = cycle of threshold of RBPJ expression—cycle of threshold RPLP0. One sample t test. d RBPJ expression in FLS isolated from individuals homozygous for rs874040 in the locus near the RBPJ gene (0), heterozygous (1), or homozygous for the wild-type variant (2). Upper extremity joints included joints of the hand, elbows, and shoulders; lower extremity joints included hips, knees, and joints of the feet. One-way ANOVA. e Expression of HES1 in the same FLS cohort. One-way ANOVA. f RBPJ expression in individuals with joint pain, but no histological signs of arthritis (arthralgia), OA and RA. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction