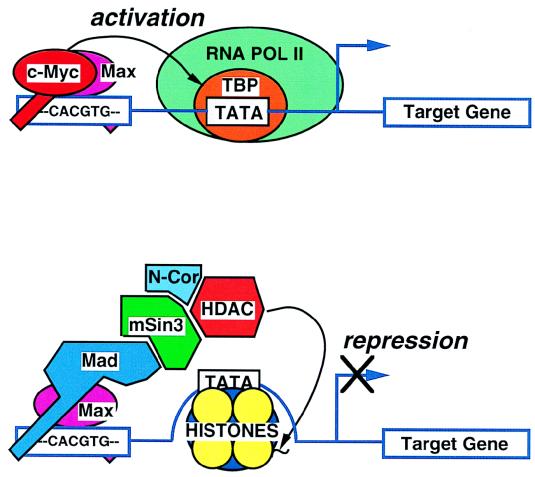
FIG. 3.
Models of c-Myc/Max and Mad/Max in transcriptional regulation. The c-Myc/Max heterodimer is shown at the top tethered to the E box 5′-CACGTG-3′. c-Myc contacts TBP, although the molecular mechanisms involved in c-Myc transactivation are not known. The bottom diagram depicts the association of the Mad/Max heterodimer with the E box, as well as with mSin3, N-Cor, and histone deacetylase (HDAC). HDAC deacetylates histones, causing the locking of nucleosomal DNA and, consequently, inhibition of transcription. POL, polymerase.