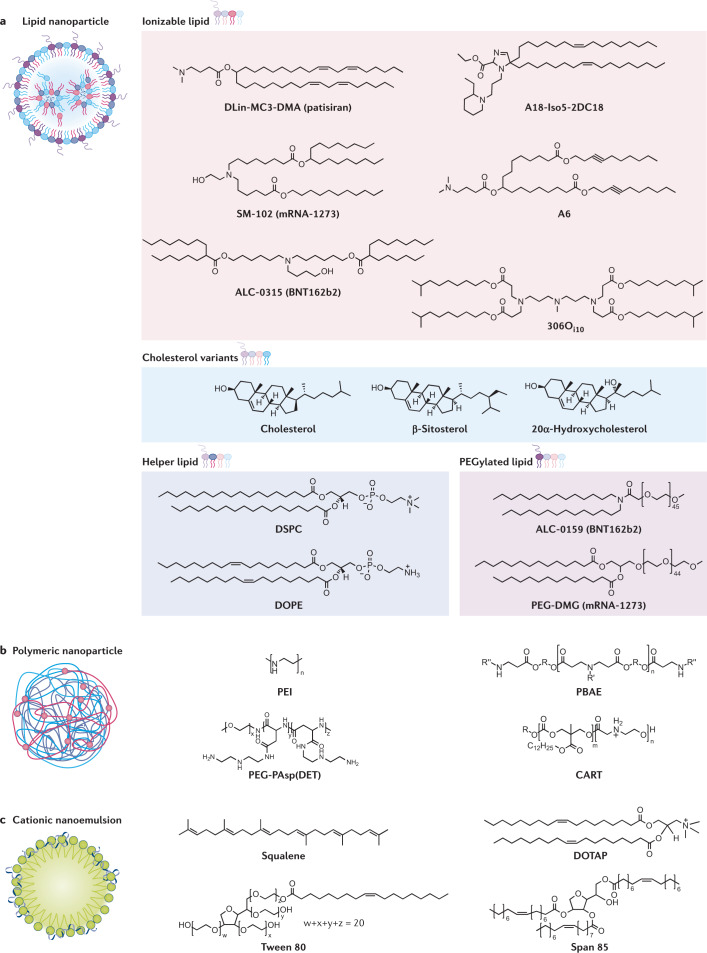
Fig. 2. All mRNA delivery vehicles contain cationic or ionizable molecules.
a | Lipid nanoparticles encapsulate mRNA in their core. They consist of four components: ionizable lipids, such as DLin-MC3-DMA42, SM-102 (ref.53), ALC-0315 (ref.54), A18-Iso5-2DC18 (ref.60), A6 (ref.57) and 306Oi10 (ref.46); cholesterol or its variants, β-sitosterol64 and 20α-hydroxycholesterol63; helper lipids, such as DSPC70 and DOPE69; and PEGylated lipids, such as ALC-0159 (ref.32) and PEG-DMG32. b | Polymers, such as PEI164, PBAE91, PEG-PAsp(DET)94 and CART99 form polymer–mRNA complexes. c | Cationic nanoemulsions contain a squalene core surrounded by an outer shell made of cationic lipid (for example, DOTAP) and surfactants, such as Tween 80 and Span 85. The mRNA adsorbs to the surface via electrostatic binding109.