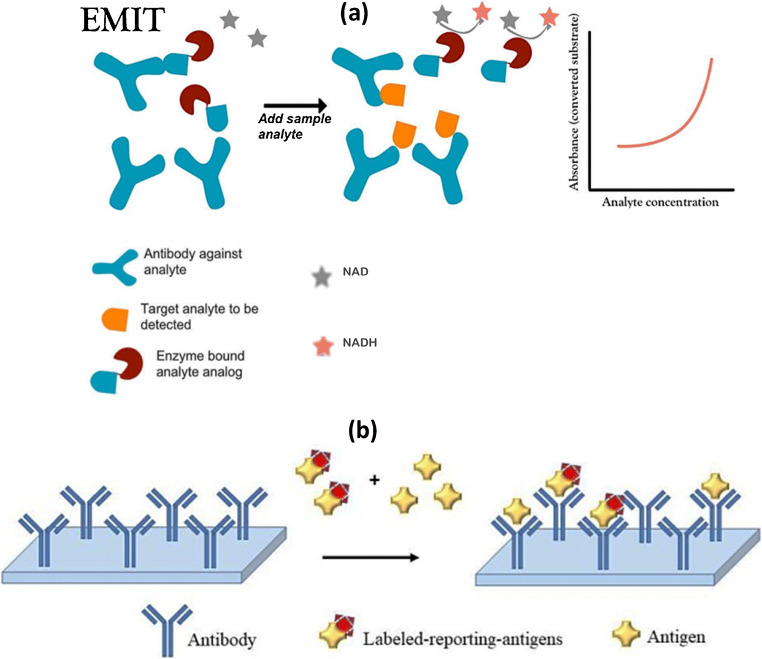
Fig. 5.
Competitive laboratory immunoassays for small molecules. a Principle of EMIT (Enzyme Multiplied Immunoassay Technique) [153]. EMIT is a competitive immunoassay in homogenous phase in which an analyte analog is bound to an enzyme using nicotinamide-adenine-dinucleotide (NAD) as a cofactor. The enzymatic reaction generates NADH which is detected by spectrophotometry at 340 nm. A competition between the analyte and the enzyme bound analog takes place toward the antibody. The amount of NADH produced is directly related to the amount of analyte present in the sample. b Competitive ELISA [154]: Antibodies are immobilized on the solid support. A competition takes place between an analyte analog coupled to an enzyme and the free analyte in the sample. The detection is achieved through enzymatic activity