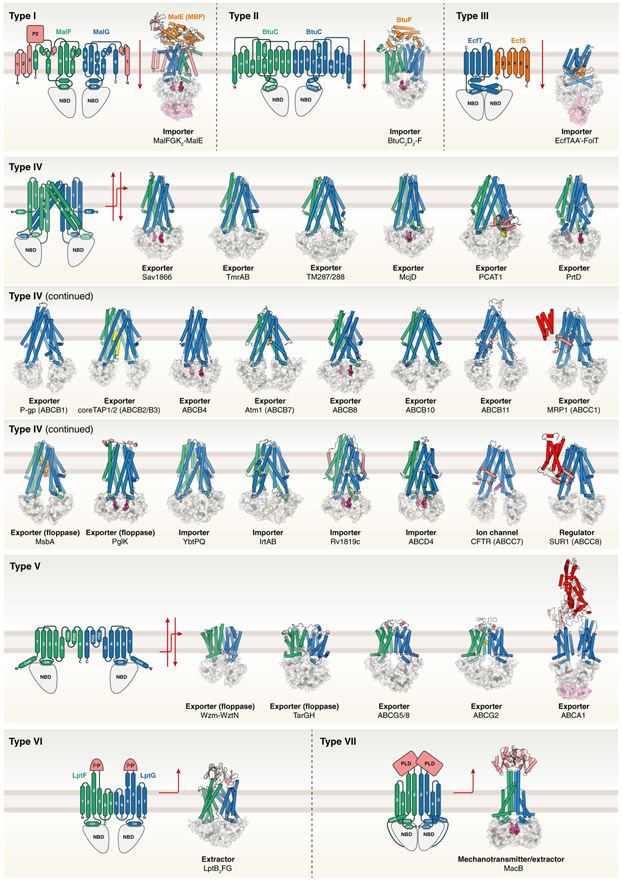
Fig. 1.
The different types within the ABC transporter superfamily. Members of the superfamily of ABC transporters can be grouped into distinct types based on their TMD fold. The TMDs of representative experimentally determined structures are depicted as cartoons, and their NBDs are shown in surface representation. The TMD architecture of the first structure of each type is illustrated by a topology diagram. The number of structures shown for each transporter type does not necessarily reflect the abundance or importance of the respective type, but highlights the common scaffold and functional diversity of the transporters. The two TMDs of each transporter are shown in green and blue, respectively, except for cases where the TMDs are part of the same polypeptide chain (uniform blue color). Please note that the type V ABC transporters also include the retina-specific importer ABCA4 and importers in plants. Substrate-binding components of type I-III folds are illustrated in orange, and auxiliary domains and additional (TM) helices are shown in red, salmon, and violet, respectively. Bound (occluded) nucleotides and Mg2+ ions in the NBDs are shown as dark pink spheres. Transported substrates and inhibitors are shown in yellow (carbon) and in CPK colors (remaining atoms in small-molecule compounds), respectively. The directions of substrate transport are indicated by solid and dashed red arrows. The structures have the following Protein Data Bank (PDB) accession codes: MalFGK2-MalE: 2R6G [12]; BtuC2D2-BtuF: 4FI3 [50]; EcfTAA′-FolT: 4HUQ [14]; Sav1866: 2HYD [15]; TmrAB: 5MKK [51]; TM287/288: 4Q4H [52]; McjD: 4PL0 [53]; PCAT1: 6V9Z [54]; Atm1: 4MYH [55]; MRP1: 5UJA [56]; PrtD: 5L22 [57]; P-gp: 4M1M [58]; TAP1/2: 5U1D [59]; ABCB4: 6S7P [60]; ABCB8: 5OCH; ABCB10: 3ZDQ [61]; ABCB11: 6LR0 [62]; MsbA: 5TV4 [63]; PglK: 6HRC [64]; YbtPQ: 6P6J [31]; IrtAB: 6TEJ [32]; Rv1819c: 6TQF [33]; ABCD4: 6JBJ [30]; CFTR: 5UAK [65]; SUR1: 6BAA [66]; Wzm-WztN: 6OIH [25]; TarGH: 6JBH [26]; ABCG5/8: 5DO7 [16]; ABCG2: 6HCO [67]; ABCA1: 5XJY [23]; LptB2FG: 5X5Y [17]; MacB: 5LJ7 [21]. ABC, ATP-binding cassette; β-jr, β-jellyroll-like domain; C, C terminus; CH, coupling helix; CoH, connecting helix; EH, elbow helix; N, N terminus; NBD, nucleotide-binding domain; P2, extracytoplasmic loop; PG, periplasmic gate helix; PLD, periplasmic domain; TMD, transmembrane domain.