Figure 2.
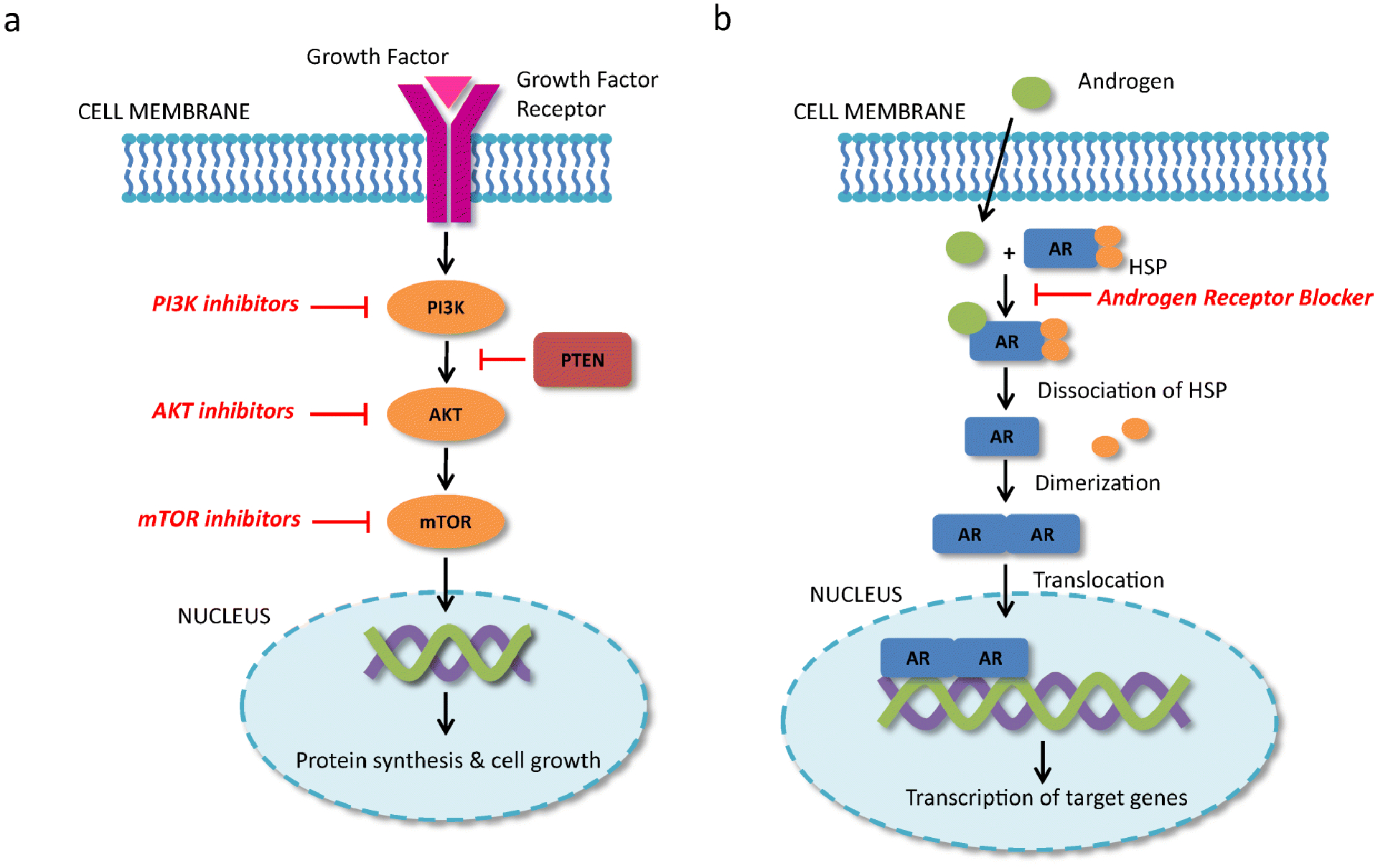
Mechanism of action of PI3K/AKT/mTOR (PAM) pathway inhibitors and androgen receptor blockers. (A) Growth factor binds to growth factor receptor in the tumor cell membrane resulting in activation of the PI3K, AKT, and mTOR. Activation of mTOR results in protein synthesis and cell growth. PTEN downregulates PI3K and results in decreased activation of the PAM pathway. PI3K, AKT, and mTOR inhibitors block the activation of this pathway and results in cell death. (B) Androgens bind to cytoplasmic androgen receptors resulting in activation. Heat shock proteins bound to the androgen receptor dissociate and the androgen receptor dimerizes. The dimer is translocated to the nucleus where it binds to the promoter region and results in gene transcription. Androgen receptor blockers block androgen binding to androgen receptor. PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinse, AKT: protein kinase B, mTOR: mechanistic target of rapamycin, PTEN: phosphatase and tensin homolog. AR: Androgen receptor, HSP: heat shock protein
