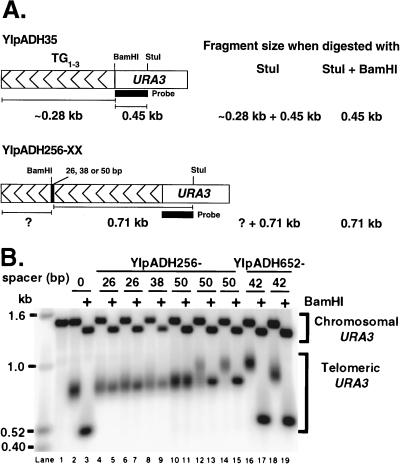
FIG. 2.
Some of the internal TG1-3 sequences are considered part of the telomere across a 50-bp nontelomeric spacer. (A) Predicted sizes of the telomere restriction fragments on Southern blots. Telomere length, i.e., the length of the elongated terminal TG1-3 tract, was determined by subtracting the StuI-BamHI fragment length from the StuI fragment length measured on the same blot. Analysis on the same blot was important for giving reproducible and accurate length determination for different control telomeres. With lanes 14 and 15 of B as an example, the length of the elongated terminal TG1-3 sequences (the ? in the diagram) is 150 bp. (B) Representative genomic DNAs from cells bearing the YIpADH256-26, -38, and -50 telomeres and the YIpADH652-42 telomere were cleaved with StuI or StuI plus BamHI and analyzed by Southern blotting using the URA3 fragment in panel A as probe. All telomeres were formed in yeast strain YM708. The 0 spacer is YIpADH35. Each pair of lanes (indicated by a bar under the number) represents an individual transformant. Lane 1, YM708 with no synthetic telomere; lanes 10 and 11, a YIpADH256-50 transformant with short telomeres; lanes 14 and 15, a YIpADH256-50 transformant with long telomeres; lanes 12 and 13, a YIpADH256-50 transformant with short and long telomeres (mixed telomeres). Note that the YIpADH652-42 construction places the BamHI site closer to URA3 (Fig. 1B). Telomere fragment sizes were determined as described in Materials and Methods.