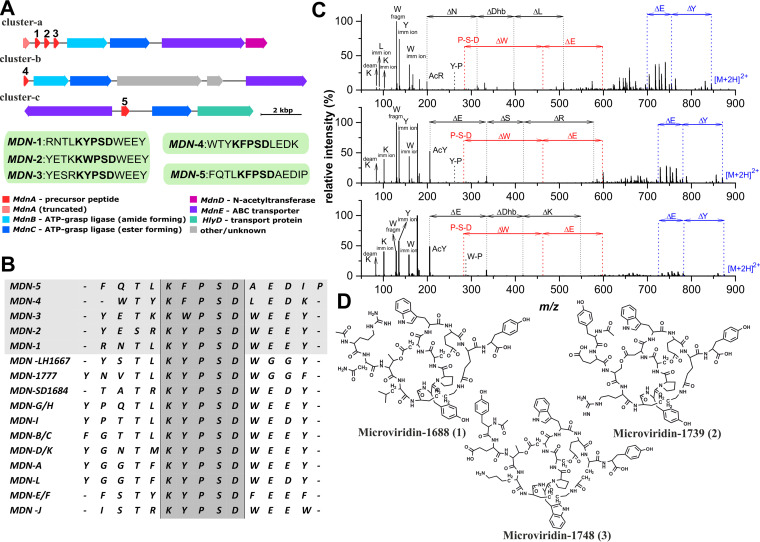
FIG 1.
(A) Gene map of microviridin gene clusters (a to c) mined from the Nostoc sp. TH1SO1 genome. For cluster a, three functional precursor peptides (MdnA) differing in the core peptide sequence are predicted, whereas for clusters b and c, each encodes a single precursor peptide. Core peptide sequences are indicated in green boxes. (B) Variation in the microviridin peptide sequence. Multiple-sequence alignment detected all five microviridin precursors (shaded in a gray background) as novel and differing from 2 to 6 amino acid positions compared to the known variants. The consensus sequence revealed the variation in the conserved motif KYPSD (shaded in dark gray) where Y (Tyr) was replaced by F (Phe) and W (Trp). The conservation of the KYPSD core motif of MDN is postulated to possess relevance to the bioactivity and ecological role of the MDNs (20). (C) HRMS/MS product ion spectra of protonated microviridins from Nostoc sp. TH1SO1. (D) Structures of the three detected microviridins, microviridin-1688 (m/z 844.8917 [M + 2H]+), microviridin-1739 (m/z 870.3707 [M + 2H]+), and microviridin-1748 (m/z 874.8821 [M + 2H]+), confirmed by coupling product ion spectra and genomic data.