Figure 1.
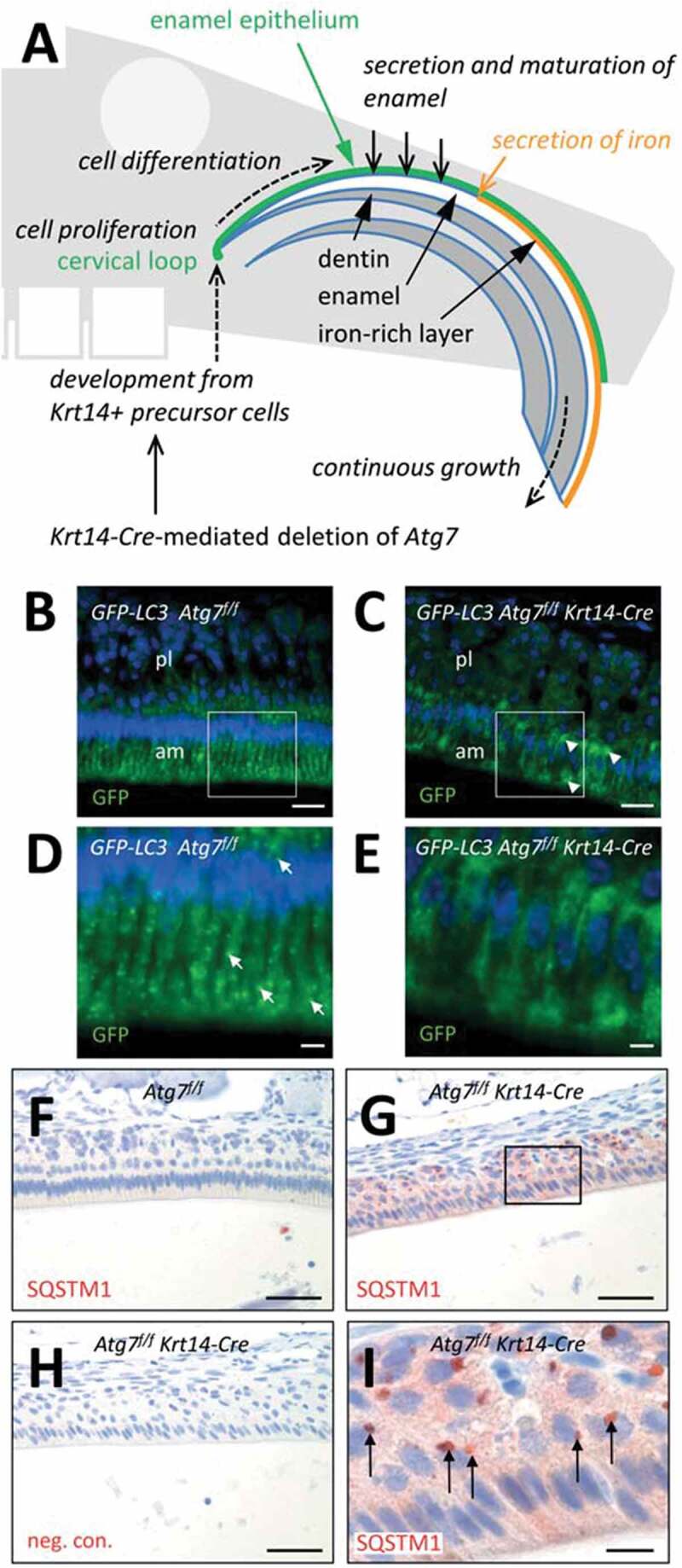
Suppression of autophagy in the enamel epithelium of Atg7f/f Krt14-Cre mice. (A) Schematic depiction of structure and growth of a murine maxillary incisor. Ameloblasts proliferate in the cervical loop and subsequently differentiate to produce enamel, including a superficial iron-rich layer. (B-E) The Gfp-Lc3 transgene was introduced into Atg7f/f (B, D) and Atg7f/f Krt14-Cre (C, E) mice. Upper jaws were sectioned and immuno-labeled with anti-GFP (green). Nuclear DNA was labeled with Hoechst dye (blue). Panels D and E show higher magnifications of the boxed areas in panels B and C, respectively. Arrows in D mark GFP-LC3-positive vesicles. am, ameloblasts; pl, papillary layer. (F-I) Immunostaining of the autophagy substrate SQSTM1. Sections through the enamel organ of Atg7f/f (F) and Atg7f/f Krt14-Cre (G-I) mice were immunostained for SQSTM1 (red). A negative control staining of Atg7f/f Krt14-Cre tissue is shown in panel H. Scale bars: 20 µm (B, C), 5 µm (D, E), 50 µm (F-H), 10 µm (I).
