Figure 3.
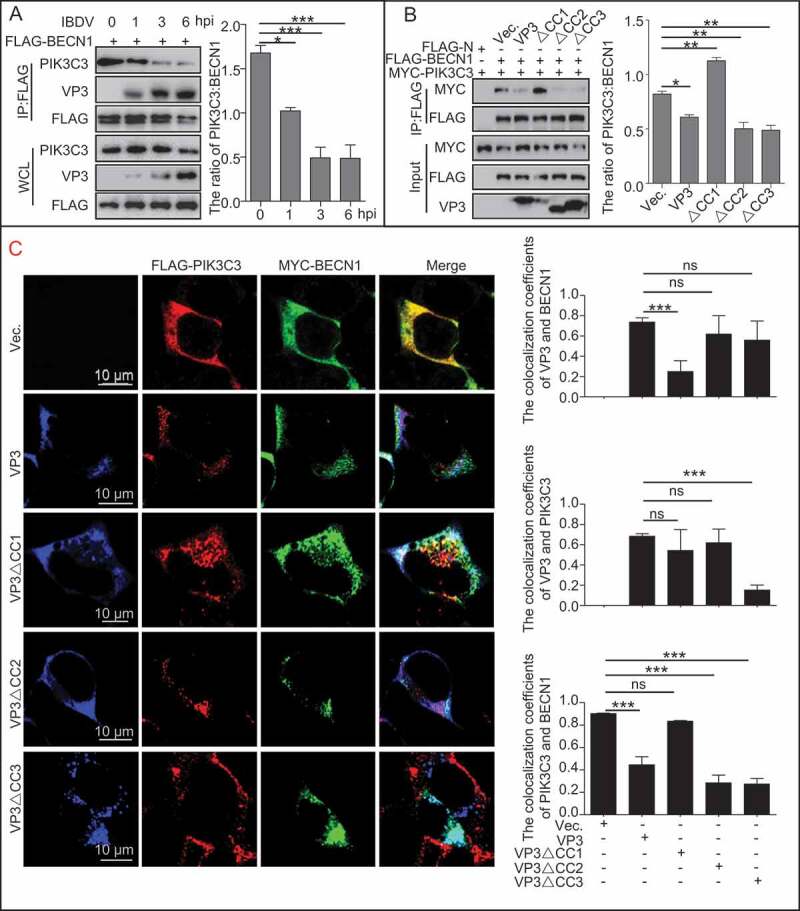
The effect of VP3 coiled-coil domains on interaction between PIK3C3 and BECN1. (A) PIK3C3’s interaction with BECN1 was gradually inhibited during Avibirnavirus infection. HEK293T cells were transfected with FLAG-BECN1 for 24 h, and then infected with Avibirnavirus at MOI = 10 for 0, 1, 3, and 6 h. The resultant cell lysates were subjected to FLAG-precipitation and immunoblotting analysis. (B and C) CC1 domain is necessary for disrupting the interaction between PIK3C3 and BECN1. HEK293T cells were transiently co-transfected with empty N-terminal FLAG-tagged vector (FLAG-N), FLAG-BECN1, MYC-PIK3C3 and VP3, ∆CC1, ∆CC2 or ∆CC3 for 24 h in 293T cells. On the one hand, cell lysates were subjected to analysis of FLAG-precipitation and immunoblotting analysis (B). On the other hand, cells were fixed and performed confocal analysis. 20 cells for each colocalization were counted. Quantitative analysis of colocalization coefficient was performed (C). Error bars: Mean ± SD of 3 independent tests. One-way ANOVA; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 compared to control.
