Figure 5.
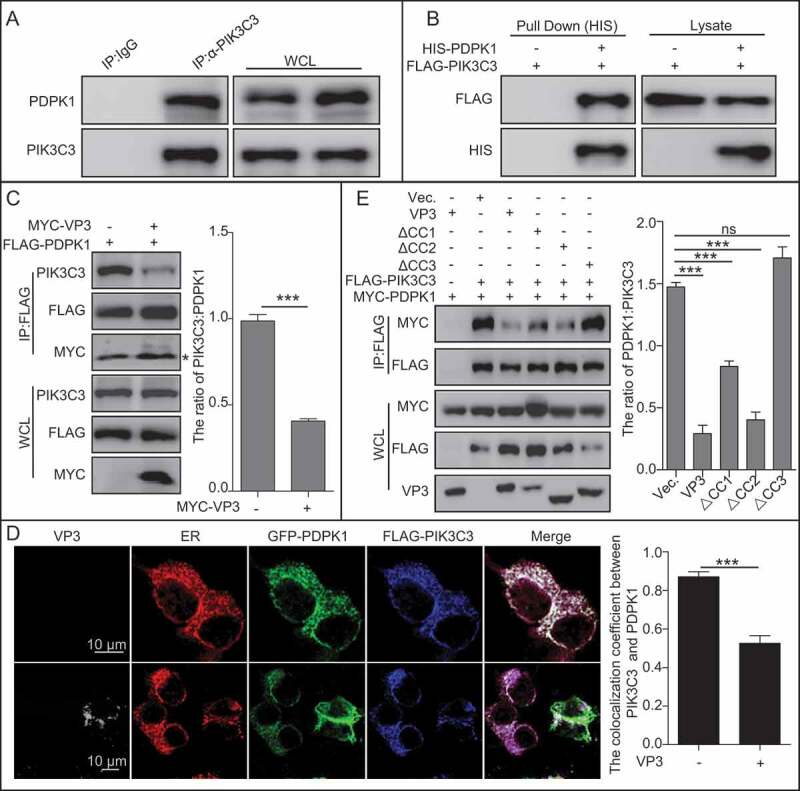
VP3 inhibits interaction between PIK3C3 and PDPK1 through CC3 domain. (A) Endogenous PIK3C3 interacts with endogenous PDPK1. Anti-PIK3C3 IP and immunoblotting analyses using anti-PIK3C3 or anti-PDPK1 antibodies were performed with whole 293T cell lysate. (B) Affinity-isolation analysis of interaction between PIK3C3 and PDPK1. HIS-PDPK1 expressed in prokaryotic cells was purified and then incubated with FLAG-PIK3C3 extracted from its expression 293T cells. In vitro affinity isolation and immunoblotting analyses using anti-FLAG or anti-HIS antibodies were performed. (C) The interaction of PIK3C3 with PDPK1 was inhibited by VP3. HEK293T cells were transiently co-transfected with FLAG-PDPK1 and MYC-VP3 for 48 h. Cellular lysates was subjected to FLAG-precipitation and immunoblotting analysis of PIK3C3, PDPK1, and VP3. * indicated light chain of antibody. (D) Colocalization analysis of VP3 with PDPK1, and PIK3C3 and the ER, in HEK293T cells. HEK293T cells were transiently co-transfected with four vectors DsRed-ER, GFP-PDPK1, FLAG-PIK3C3, and pCI-neo-VP3 (VP3) for 24 h. Cells were immunostained with anti-FLAG and anti-VP3 monoclonal antibodies and were observed using confocal microscopy. Scale bar: 10 μm. (B) Quantitative analysis of the numbers of puncta. (E) The CC3 domain of VP3 is critical for blocking PIK3C3 interaction with PDPK1. HEK293T cells were transiently co-transfected with FLAG-PIK3C3, MYC-PDPK1, pVP3, pVP3△CC1, pVP3△CC2 and pVP3△CC3 for 48 h. Cellular lysates were subjected to FLAG-precipitation and immunoblotting analysis of PIK3C3, PDPK1, VP3, VP3△CC1, VP3△CC2, and VP3△CC3. Error bars: Mean ± SD of 3 independent tests. One-way ANOVA; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 compared to control.
