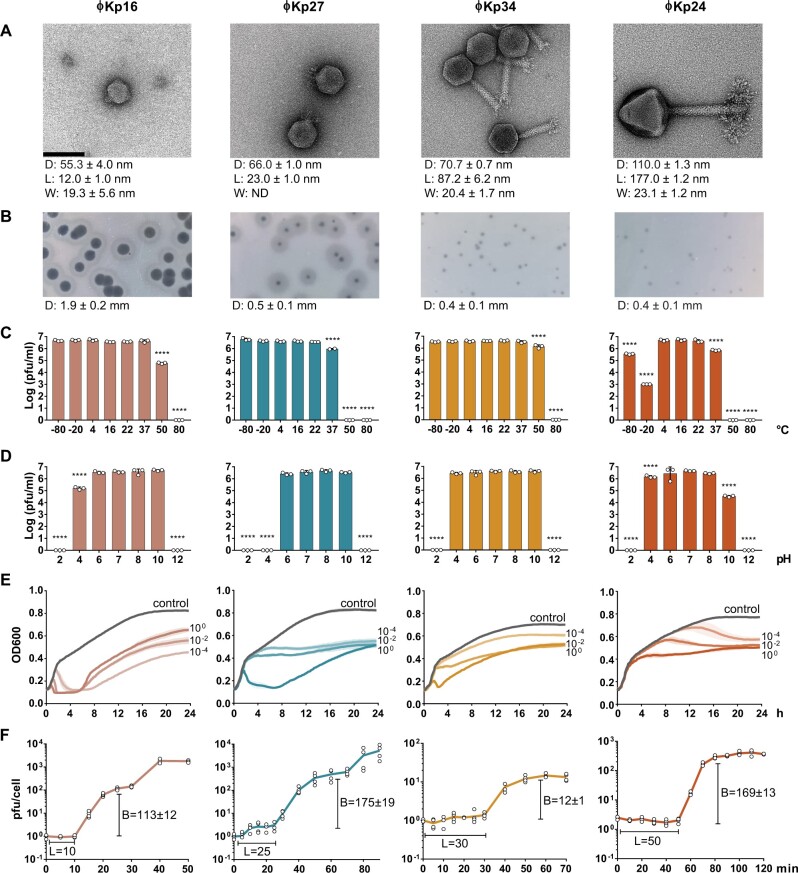
Figure 1.
Morphological and phenotypic features of four newly isolated Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteriophages. (a) Transmission electron microscopy images of Autographiviridae ϕKp16, Autographiviridae ϕKp27, Myoviridae ϕKp34, and Myoviridae ϕKp24. Bacteriophages were negatively stained with 2% uracyl acetate. The diameter (D) of the capsid, and the length (L), and width (W) of the tail are given in nanometres below each phage as the average dimensions of 10 phage particles. Bar: 100 nm. All micrographs were taken at ×200,000 magnification. (b) Morphology of phage plaques. The diameter (D) of the plaque is given in millimetres below each phage as the average dimension of 10 phage plaques. (c) Viability of the phages at different temperatures. (d) Viability of the phages at different pH values. (e) Effect of the phages on cell growth of their isolation strain, measured as optical density at 600 nm. Control represents the growth of the strain without phage, while the remaining curves represent growth of the strain when infected with phage at a multiplicity of infection of 100, 10−2, or 10−4. (f) One step growth curve of the phages. The burst size (B) and latency period (L) are given in pfu and min, respectively.