Figure 4.
The relative importance of the newborn gut microbiota in predicting rapid infant growth compared to known clinical predictors
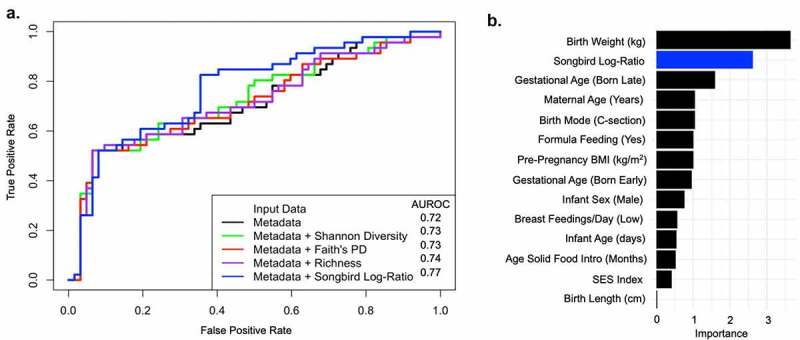
Figure 4. (a) The area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve using leave-one-out predictions for rapid growth using a random forest classifier. The AUROC is indicated in the legend. The metadata correspond to known clinical predictors, including maternal age at birth (years), pre-pregnancy BMI (kg/m2), delivery mode (vaginal, c-section), measures of socioeconomic status (SES), infant age and sex, birth weight (kg) and length (cm), breast feedings per day (≥8, <8), formula feeding (yes/no), age of solid food introduction (days), and time of delivery (on-time, early [>2 weeks before due date], late [>2 weeks after due date]). (b) Importance based on variable importance (VIP) scores where a higher importance score indicates a greater contribution of each variable in predicting rapid infant growth. The Songbird log-ratio corresponds to the curated selection of the log-ratio of the top- and bottom 40% ranked sOTUs that were differentially associated with rapid infant growth in the first year of life.
