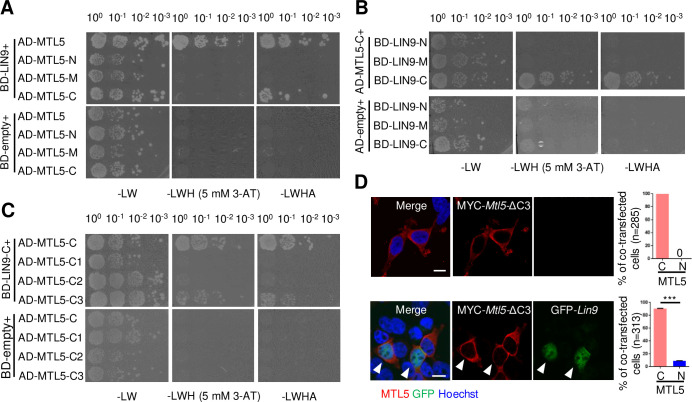
Fig 4. LIN9 directly interacts with MTL5 C-terminal residues 443–475 for transport of MTL5 into the nucleus.
(A) The Y2H was used to assess the interaction of truncated MTL5 (MTL5-N, MTL5-M, and MTL5-C) with full length LIN9, respectively. MTL5-N contains residues 1–250 aa;MTL5-M contains residues 251–370 aa;MTL5-C indicates contains 371–475 aa. (B) Y2H assessment of interactions between of truncated LIN9 (LIN9-N, LIN9-M, and LIN9-C) with AD-MTL5-C (371–475 aa) respectively. LIN9-N contains residues 1–150 aa;LIN9-M contains residues 151–340 aa;LIN9-C contains residues 341–559 aa. (C) The interactions of AD-MTL5-C1 (371–418 aa), AD-MTL5-C2 (419–442 aa), and AD-MTL5-C3 (443–475 aa) with BD-LIN9-C (341–559 aa) or BD-empty (control) was assessed by Y2H, respectively. The interaction in (A-C) was tested by growth of the yeast cells on double (SD-Leu/Trp, -LW), triple (SD-His/Leu/Trp with 5 mM 3-AT, -LWH) or quadruple dropout medium plates (SD-Ade/His/Leu/Trp, -LWHA) at different dilutions. (D) HEK293T cells were transiently co-transfected with plasmids encoding MYC-Mtl5-ΔC3 (C-terminal 443–475 aa residues were deleted) and GFP-LIN9. The localization of LIN9 and mutant MTL5 was detected by immunostaining with antibodies against GFP (green) and MTL5 (red), respectively. The nuclei (blue) of HEK293T cells were counterstained with Hoechst 33342. The cells with nuclear (N) or cytoplasmic (C) localization of MTL5 were counted and “n” in the brackets represent the number of (co-)transfected cells analyzed. White arrowheads indicates the localization of truncated MTL5 and LIN9 in HEK293T cells. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent replicates. P values were detected by Student’s t-test. ***p<0.001. Scale bar, 10 μm.