Fig. 2. Adhesion tests of HPC hydrogels.
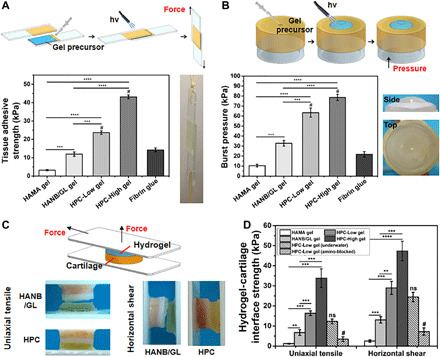
(A) Standard lap shear and (B) burst pressure tests to determine the hydrogel-tissue binding strength of the HPC hydrogels compared with those of HAMA gel, HANB/GL gel, and Fibrin glue (commercially available sealant). Schematic illustration (top) and photographs (right) of the modified standard methods for lap shear and burst pressure tests. (C) Schematic illustration (top) and photographs (bottom) of the uniaxial tensile and horizontal shear tests of the HPC or HANB/GL gel-cartilage interface strength. (D) Hydrogel-cartilage interface strength measured by tensile and shear tests. For the amino-blocked group, the cartilage was preprocessed by 10% formaldehyde solution to block the amino groups before use. For the submerged group, the sample of gel-cartilage construct was prepared under water. Light: 395-nm LED, 50 mW/cm2. Irradiation time, 180 s. n = 4; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, and #P < 0.01 compared with the HPC-Low gel; ns, no significance. The hydrogel compositions are the same as in Fig. 1. Photo credit: Yujie Hua, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine.
