Fig. 5. Feasibility evaluation of HPC hydrogel–based arthroscopic cartilage repair under water in vitro.
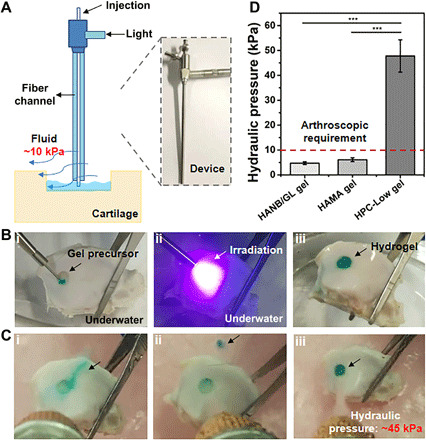
(A) Schematic illustration (left) and photograph (right) of the arthroscopic device with combined hydrogel injection tube and optical fiber channel for curing (7 mm external diameter). (B) Photographs of in vitro operation of in situ cartilage defect repair using HPC hydrogel under water: injection of gel precursor (i), light irradiation (ii), and repaired cartilage defect (iii). (C) The cured hydrogel-cartilage constructs are flushed with water at various hydraulic pressures: HANB/GL gel (i), HAMA gel (ii), and HPC-Low gel (iii). (D) Resistance to water pressure during washing of the repaired cartilage defect by HANB/GL, HAMA, and HPC-Low gels. Fast Green FCF dye is added to the hydrogel for visualization. Light: 395-nm LED, 50 mW/cm2. Irradiation time, 10 s. n = 3, ***P < 0.001. The hydrogel compositions are the same as in Fig. 1. Photo credit: Yujie Hua, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine.
