Figure 3. Phenotypic rescue effect of N,N-diethylaminobenzaldehyde (DEAB) and BMS009 on 1-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]−1H-imidazole (TRIM)-treated embryos.
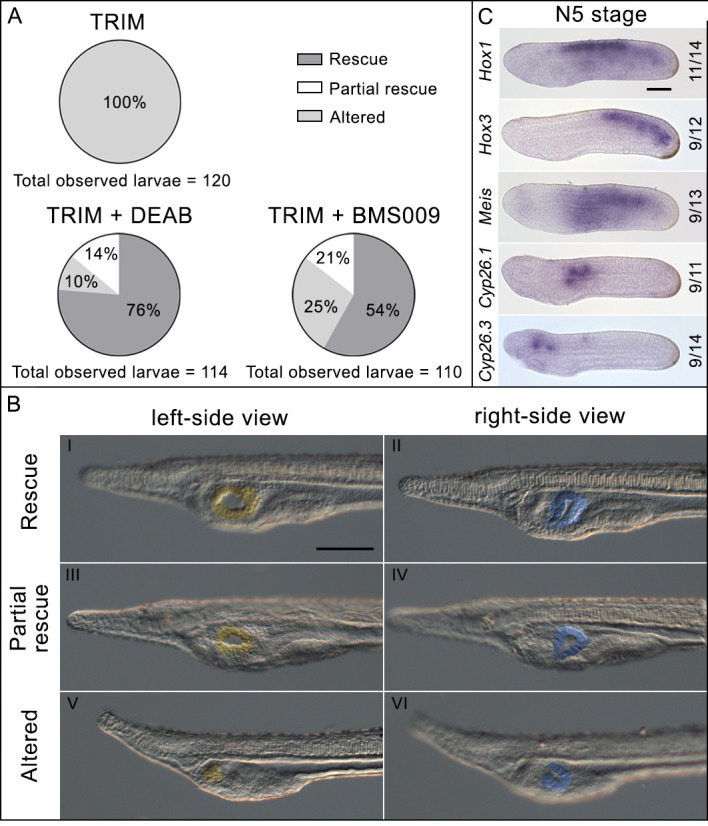
(A) Pie charts of the phenotypes observed after TRIM treatment and the combinatorial pharmacological treatments TRIM (100 µM) + DEAB (25 µM) or TRIM (100 µM) + BMS009 (10−6 M). The percentages of each observed phenotype are reported in the respective portions of the graphs. For each treatment, the total number of observed larvae is indicated below the chart. (B) Pictures of the pharyngeal region of larvae presenting the three different classes of phenotype observed in the rescue experiments: rescue, partial rescue, and altered. The mouth is highlighted in yellow and the club-shaped gland in blue. Larvae orientation: anterior to the left, dorsal to the top. Scale bar: 50 µm. (C) Expression pattern by in situ hybridization of Hox1, Hox3, Meis, Cyp26.1, and Cyp26.3 after rescue assay with DEAB showing the restoration of wild-type expression territories. Numbers indicate the ratio between embryos showing a restored expression pattern and the total number of embryos analyzed. Embryo orientation: anterior to the left, dorsal to the top. Scale bar: 50 µm.
