Figure 4. MLL-ELL transforms through the common binding platform for AF4 and EAF1.
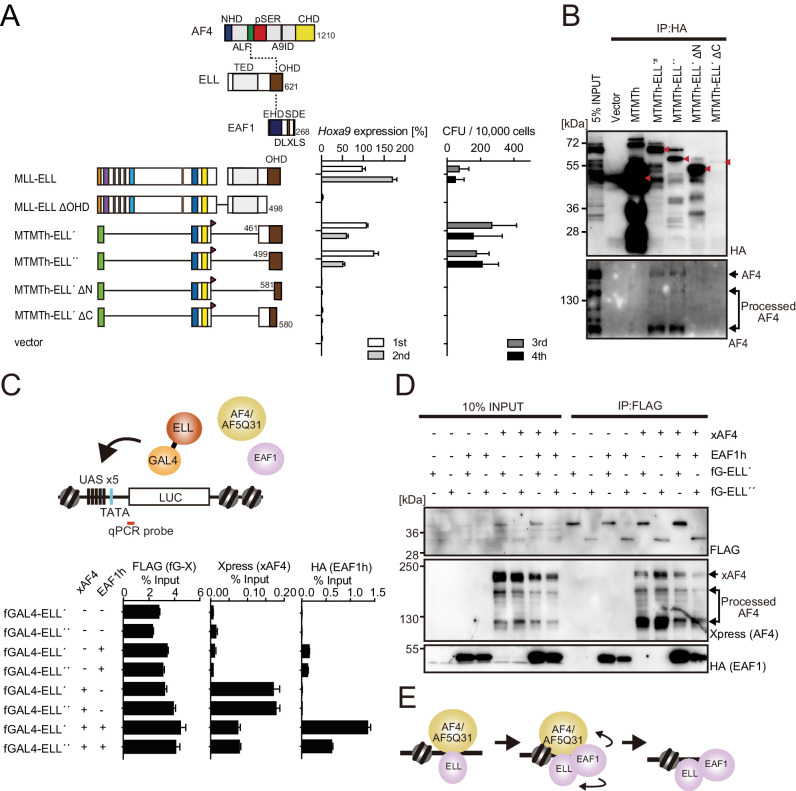
(A) Requirement of the occludin homology domain (OHD) in MLL-ELL-mediated transformation. Various MLL-ELL constructs carrying mutations in the ELL portion were examined for the transformation of myeloid progenitors, as in Figure 1A. NHD: N-terminal homology domain; ALF: AF4/LAF4/FMR2 homology domain; pSER: poly-serine; A9ID: AF9 interaction domain; CHD: C-terminal homology domain; EHD: EAF family homology domain; DLXLS: DLXLS motif; SDE: SDE motif. (B) OHD-dependent association with AF4. Immunoprecipitation (IP)-western blotting of the chromatin fraction of virus-packaging cells, transiently expressing various HA-tagged MTMT-ELL fusion constructs, was performed. Endogenous AF4 proteins co-purified with MTMTh-ELL proteins were visualized by an anti-AF4 antibody. (C) Sequential recruitment of AF4 and EAF1 by ELL. HEK293TL cells (Okuda et al., 2015), which harbor GAL4-responsive reporter, were transfected with various combinations of FLAG-tagged GAL4 fusion proteins, xAF4, and HA-tagged EAF1 (EAF1h), and were subjected to chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-qPCR analysis. A qPCR probe near the GAL4-responsive elements (UAS) was used. The ChIP signals were expressed as the percent input with error bars (mean ± SD of PCR triplicates). TATA: TATA box; LUC: luciferase. (D) Effects of overexpression of AF4 or EAF1 on ELL complex formation. IP-western blotting of the chromatin fraction of HEK293TL cells, transiently expressing various combinations of FLAG-tagged GAL4-ELL proteins, xAF4, and EAF1h, was performed. (E) A model of the sequential association between ELL, AF4 family proteins, and EAF family proteins.
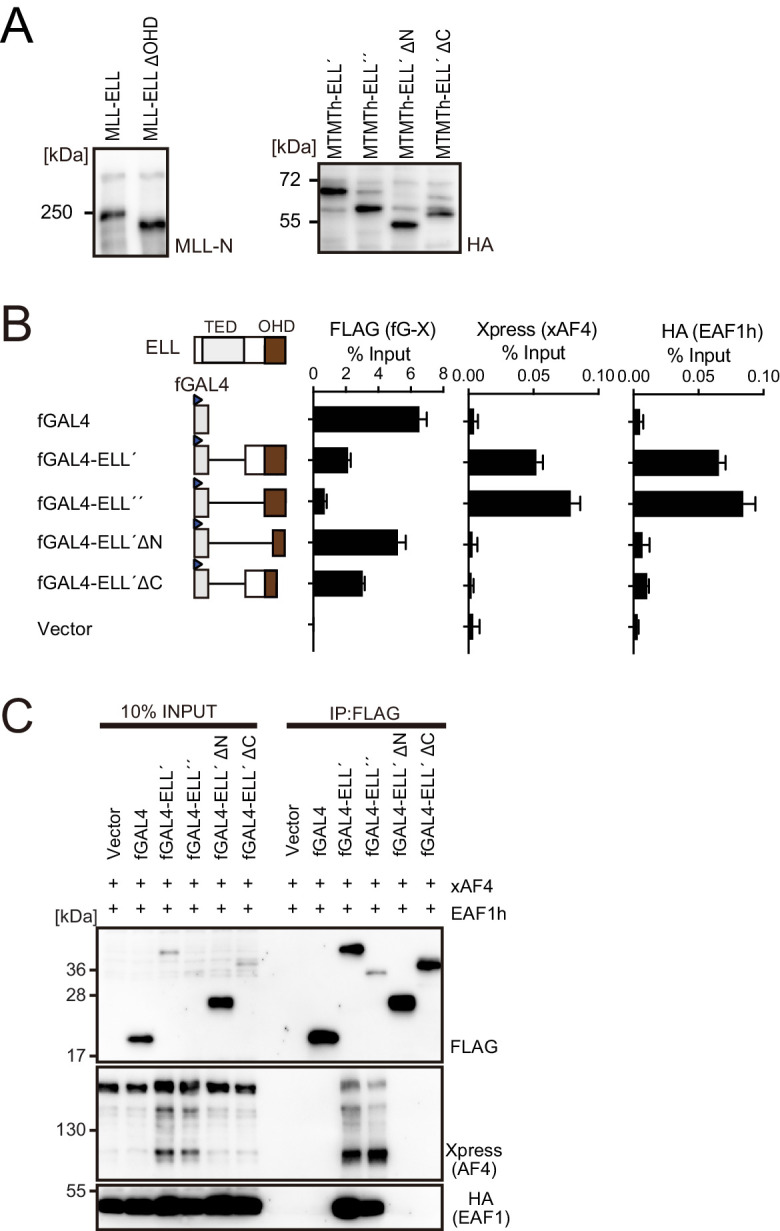
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Functions of the ELL portion.