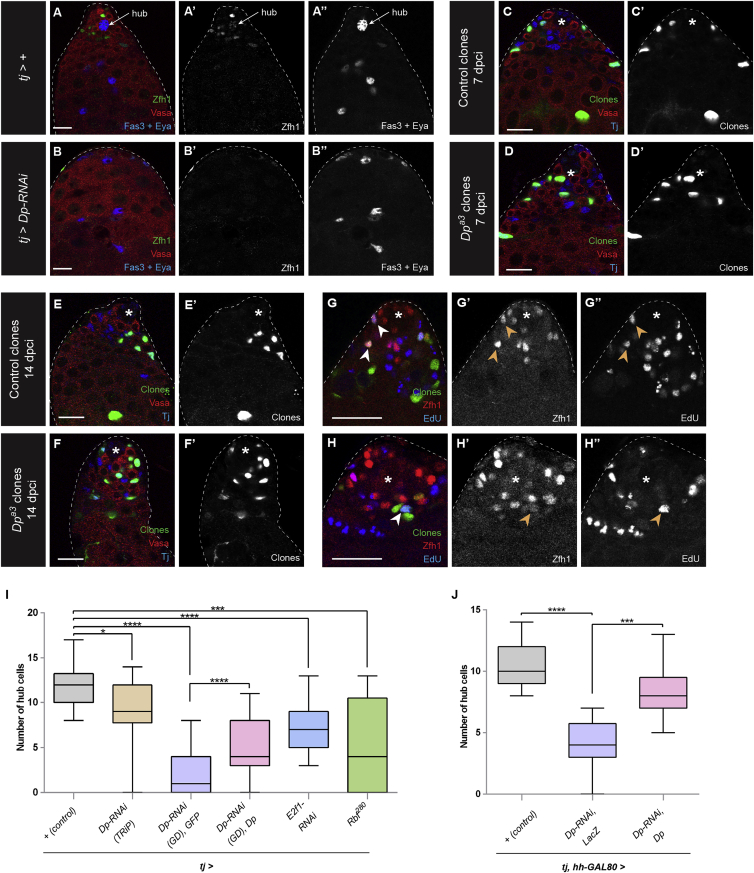
Figure 1.
Dp/E2f1 is required in CySCs to maintain hub cells
(A and B) A control tj-GAL4 (labeled tj>+) adult testis with hub cells (A, arrow) surrounded by both GSCs and CySCs. A tj>Dp-RNAi (B) adult testis lacking CySCs, GSCs, and hub cells. Both testes were isolated after 10 days at 29°C to induce maximal GAL4 activity. Zfh1 (green) labels CySCs, Vasa (red) marks the germline, Fas3 (blue) marks the hub cell membranes, and Eya (blue) labels the nucleus of differentiating cyst cells.
(C–H) GFP-positive FRT42D control clones (C, E, and G) or FRT42DDpa3 mutant clones (D, F, and H). Both types of CySC clones can be recovered at 7 days post clone induction (dpci) (C and D) and 14 dpci (E and F) and both incorporate EdU (blue, G and H), indicating that they can undergo S phase. Clones are marked by GFP (green), Vasa (red, C–F) marks the germline, and Tj (blue, C–F) marks CySCs and early cyst cells. Zfh1 (blue, G and H) marks CySCs.
(I) Graph showing the average number of hub cells after 10 days in 29°C using tj-GAL4 in control (+, gray bar, n = 18), Dp-RNAi (brown and purple bars, n = 14 and n = 31, respectively), Dp depletion plus exogenous Dp (pink bar, n = 15), E2f1 depletion (blue bar, n = 17), and overexpression of Rbf280 (green bar, n = 12).
(I and J) Graphs showing the average number of hub cells after 10 days in 29°C using tj-GAL4 and hh-GAL80, which inhibits GAL4 activity in the hub, limiting expression of UAS-dependent constructs to CySCs in control (+, gray bar, n = 27), Dp-RNAi (purple bar, n = 8), and Dp depletion plus exogenous Dp (pink bar, n = 33).
An asterisk marks the hub.
Error bars represent the data range. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗p < 0.05 as assessed by Student’s t test.
See also Tables S1 and S2; Figures S1 and S2. Scale bar, 20 μM.