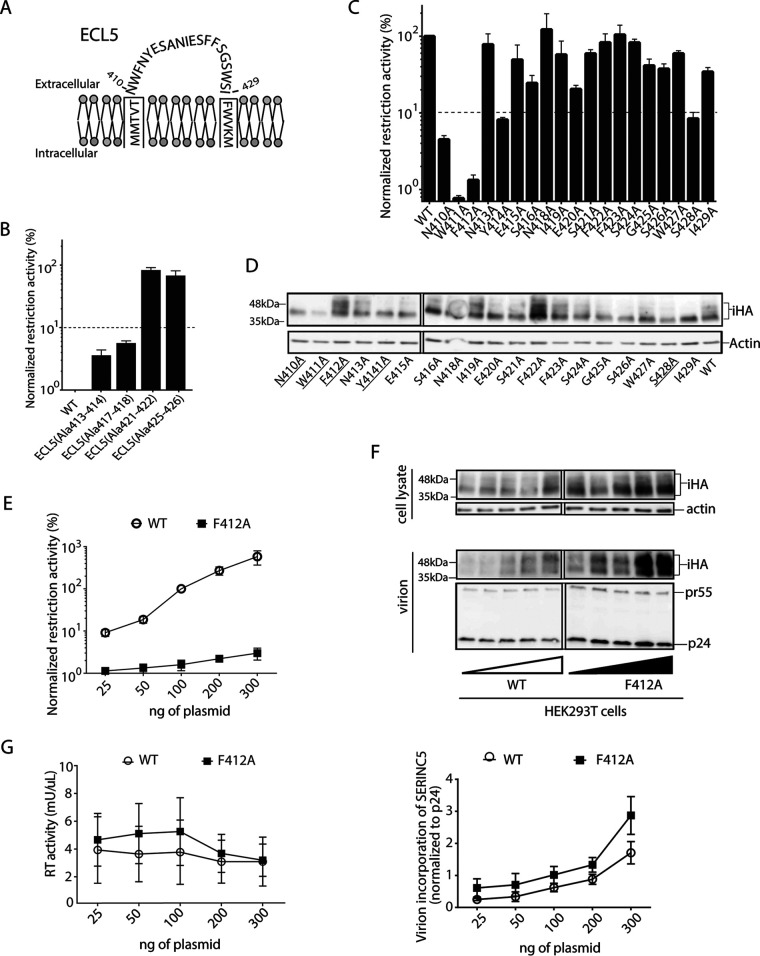
FIG 2.
Important role of F412 residue of SERINC5 in HIV-1 restriction. (A) Schematic illustration of ECL5 depicting residues N410 to W429 of SERINC5. (B and C) Restriction activity of WT and a series of the indicated ECL5 alanine insertion mutants of SERINC5-iHA (B) and of a series of alanine substitution mutants of ECL5 of SERINC5-iHA (C) against HIV-1 NL43ΔEnvΔNef pseudotyped with EnvNL that had been produced in HEK293T cells. The single-round infectivity was measured as β-galactosidase activity in TZM-bl target cells. The restriction activity was calculated as the fold difference of infectivity relative to the empty vector control, and the resultant values were normalized to SERINC5 WT, which was set to 100%. Mutants with normalized restriction activity of <10% (dotted lines) were considered to be significantly affected. (D) Immunoblots showing the steady-state cellular expression levels of the indicated WT and alanine substitution mutants of SERINC5-iHA that had been visualized with anti-HA tag antibody. Mutants with significantly reduced restriction activity are underlined. (E) Restriction activity of WT and F412A mutant of SERINC5-iHA proportional to the indicated amount of DNA at transfection. (F) Immunoblots depicting the virion incorporation levels of WT and F412A mutant with increasing transfection dosage (25 to 300 ng) (top) and virion incorporation levels of WT and the F412A mutant with increasing transfection dosage (25 to 300 ng) normalized to p24 Gag levels (bottom). (G) Virion production of HIV-1 NL43ΔEnvΔNef pseudotyped with EnvNL in the presence of increasing transfection dosage (25 to 300 ng) of the genes encoding WT and F412A SERINC5 in HEK293T cells. Culture supernatant containing viral particles was harvested and assessed for reverse transcriptase (RT) activity. The immunoblot shown is representative of 3 independent replicates. Data are means and SD from 3 independent experiments.