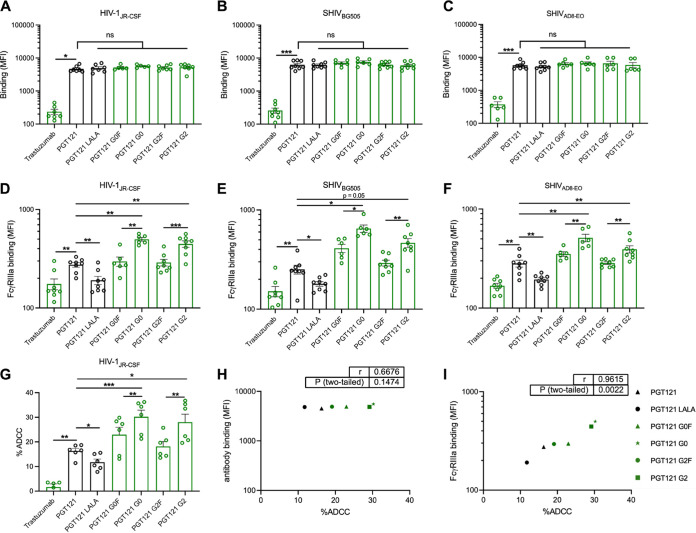
FIG 4.
Fc glycosylation profile of PGT121 modulates FcγRIIIa interaction and ADCC against infected primary CD4+ T cells. Cell surface staining of primary CD4+ T cells infected with (A and D) HIV-1JRCSF, (B and E) SHIVAD8-EO, and (C and F) SHIVBG505 was performed 48 h postinfection. Antibody binding was detected either by using Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated anti-human secondary Abs (A to C) or by using biotin-tagged dimeric rsFcγRIIIa (0.2 μg/ml) followed by the addition of Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated streptavidin (D to F). (A to F) Graphs represent MFI values in the infected population (p24+ or p27+) determined from at least five independent experiments, with the error bars indicating means ± the SEM. (G) Primary CD4+ T cells infected with HIV-1JRCSF were used as target cells. Autologous PBMCs were used as effector cells in a FACS-based ADCC assay. The graph represents the percentages of ADCC obtained in the presence of the respective antibodies. Statistical significance was tested using a paired t test or Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test based on statistical normality (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, nonsignificant). Black histogram bars represent 293F cell-derived MAbs, and green histogram bars represent plant-derived MAbs. (H and I) Correlations between the levels of ADCC and levels of antibody binding (H) or FcγRIIIa binding (I), as measured on primary CD4+ T cells infected with HIV-1JRCSF. Statistical significance was tested using a Pearson correlation test. Black points represent 293F cell-derived MAbs, and green points represent plant-derived MAbs.